-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
SPI
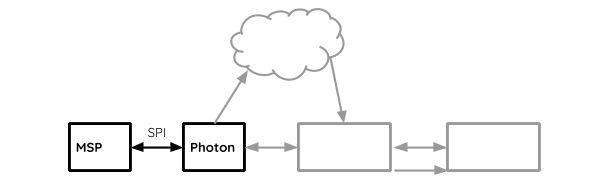
The amount of data transmitting between the Photon and the MSP430 is relatively large, therefore SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is chosen since it is fast and does not take too many I/O pins.
Because SPI communicates by swapping data, the measurements of the robot such as line sensor reading can be transmitted to the Photon at the same time as the MSP itself receives parameters or commands from the web.
The data simultaneously transmitted between these two devices are put into two arrays that together are called Infoboard. Each device has a copy of the Infoboard, and will update each other with their half of the board.
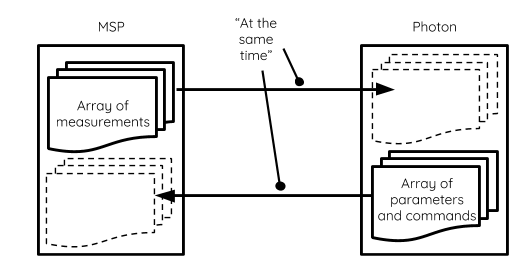
Very rarely, a miscommunication will occur due to timing error between devices. This is especially troublesome for the controller since the data passed from the Photon are parameters used for the control system. An error in that data will cause the robot to exhibit unexpected and undesirable behaviour.
Tuning the SPI transmission to be flawless is impossible given the time constraint and all the software layers that would need to comply, so a checksum algorithm is used to detect and discard corrupted data.
The algorithm of choice was the CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check), which is the simplest algorithm that meets all the three requirements for such problem:
- Detection of simple bit errors
- Detection of burst errors (Many errors in a row), common in SPI timing errors
- Detection of shift errors (Bytes out of order), a real possibility in SPI timing errors
- Relatively low cost computation (utilizes XOR and SHIFT operations mostly)
A sample code for CRC was reverse engineered and adapted to work with our system.