-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.8k
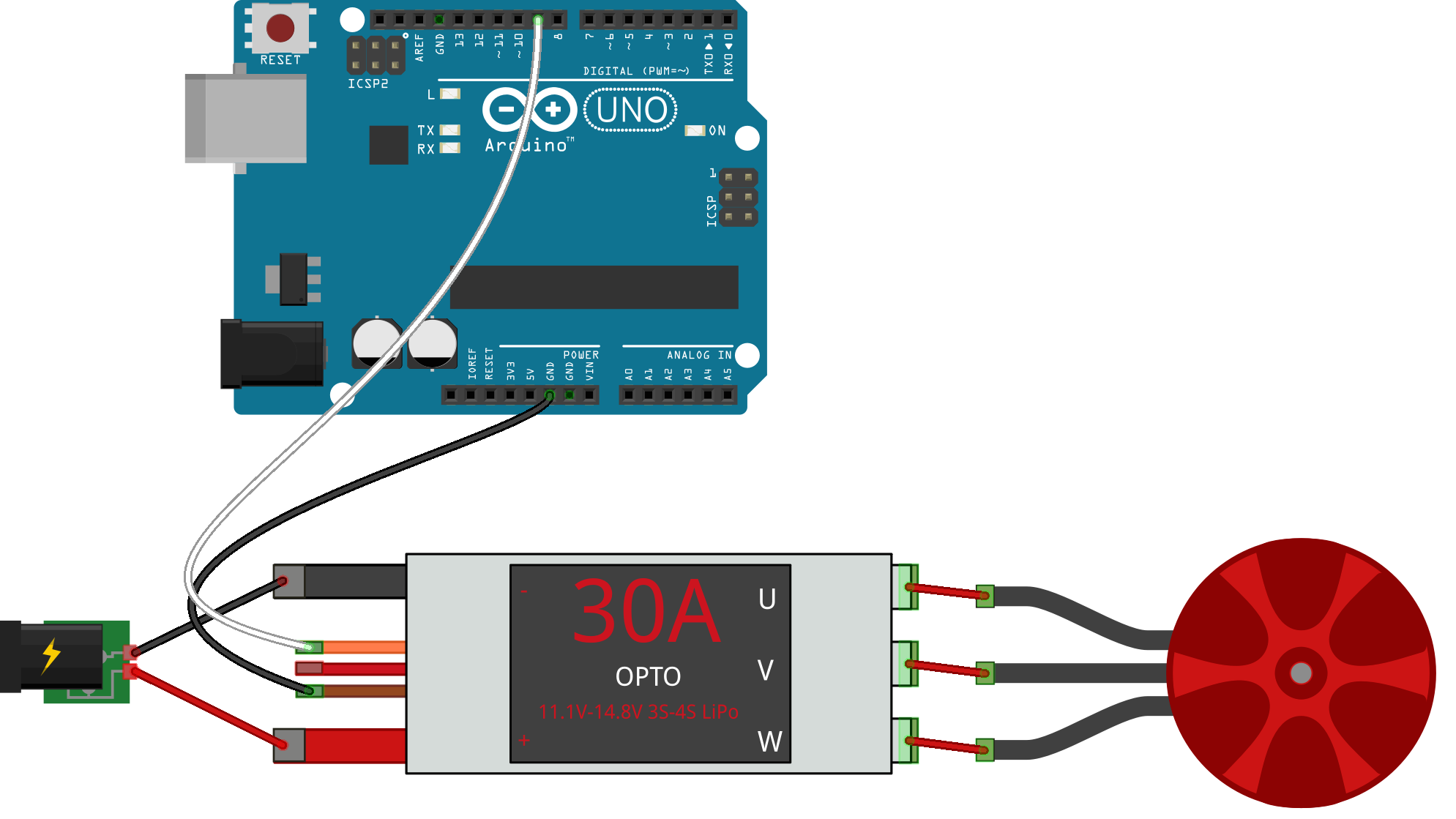
The ESC class constructs objects that represent a single ESC (Electronic Speed Control) component attached to the physical board. ESC objects are similar to Servo objects as they both use PWM pins to communicate with the physical ESC. Currently, this class assumes the ESC is pre-calibrated.
See also:
-
pin A Number or String address for the ESC pin (PWM).
var esc = new five.ESC(9);
-
Options An object of property parameters.
Property Type Value/ Description Default Required pin Number, String Any PWM Pin. The address of the PWM pin the ESC is attached to yes controller String DEFAULT, PCA9685. Controller interface type. "DEFAULT" no pwmRange Array [ min, max ]The pulse width range in microseconds.[1000, 2000]no device String FORWARD, FORWARD_REVERSE, FORWARD_BRAKE_REVERSE. Device capability type. "FORWARD" no neutral Number Neutral point, usually the middle of the PWM range. Varies by deviceno -
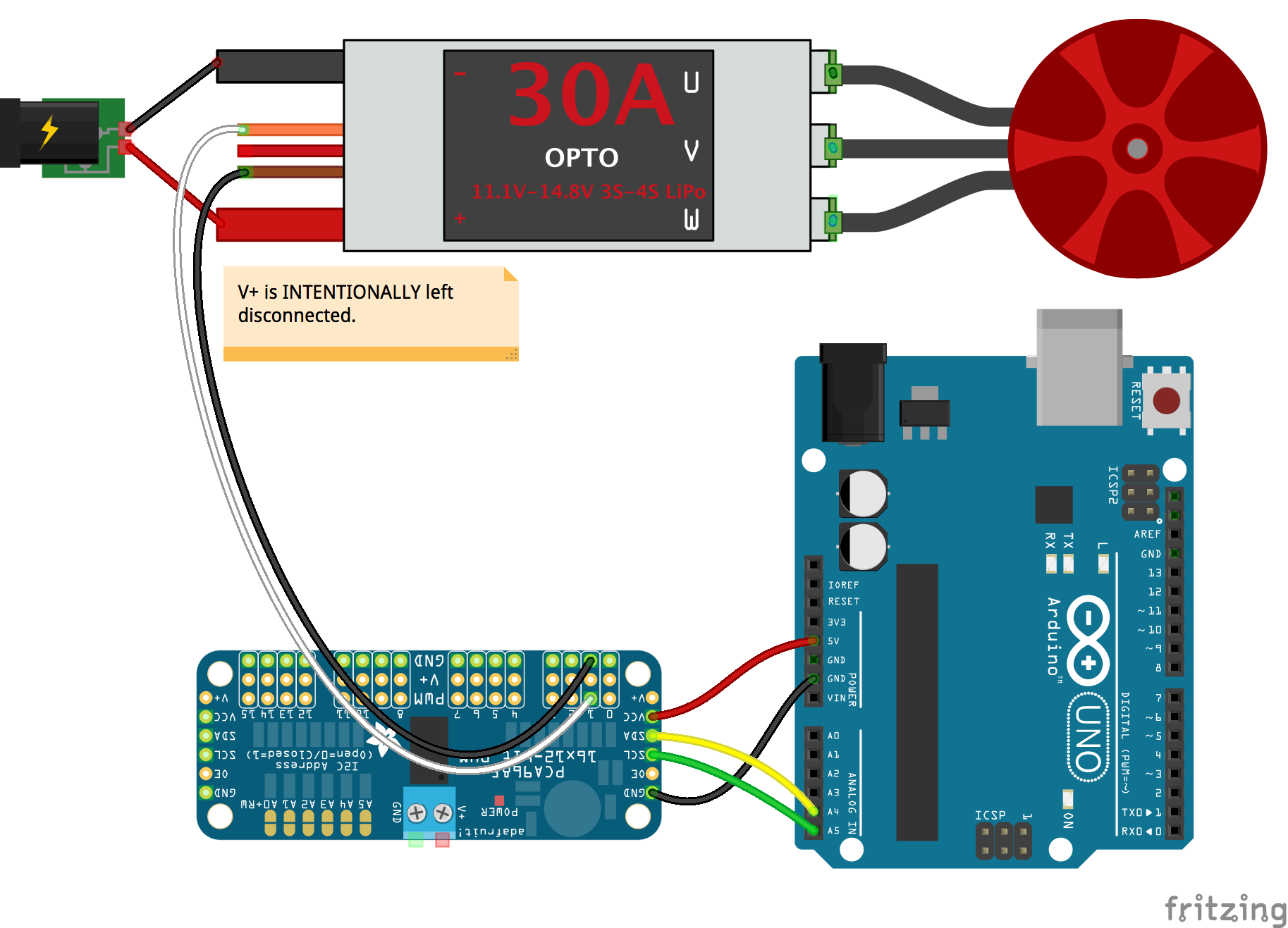
PCA9685 Options (
controller: "PCA9685")Property Type Value/Description Default Required address Number I2C device address. 0x40no
| Property Name | Description | Read Only |
|---|---|---|
id |
A user definable id value. Defaults to a generated uid | No |
pin |
The pin address that the ESC is attached to | No |
neutral |
The stopped/brake-state value of the ESC, usually the middle of PWM range. | No |
pwmRange |
[ min, max ] The pulse width range in microseconds. |
No |
new five.ESC(9);new five.ESC({
device: "FORWARD_REVERSE",
controller: "PCA9685",
pin: 1
});new five.ESC({
device: "FORWARD_REVERSE",
pin: 9,
});Standard, FORWARD-only ESC:
const five = require("johnny-five");
const board = new five.Board();
board.on("ready", function() {
const esc = new five.ESC(11);
const speed = 0;
board.loop(100, () => {
// limit to 10% for safety!
if (speed < 10) {
speed += 1;
esc.throttle(speed);
}
});
});-
speed(value) Deprecated. Use
throttle(μs)orthrottle(%) -
throttle(μs|percentage) Throttle the speed of the ESC by setting a pulse in μs or percentage (0-100).
var esc = new five.ESC(9); esc.throttle(1500); // 1500μs is half speed of a single direction or neutral of a bidirectional esc.throttle(50); // 50% is half speed in a single direction or neutral of a bidirectional
-
brake() Brake the ESC
var esc = new five.ESC(9); esc.brake();
This isn't a requirement, but if you experience issues with your ESCs, it might prove helpful
Load the following sketch onto your Arduino, via the Arduino IDE follow the instructions.
This requires that the ESC's power source is off or disconnected at the start of the calibration process. You will be prompted to turn on/reconnect the power during the process.
#include <Servo.h>
#define MAX_SIGNAL 2000
#define MIN_SIGNAL 1000
#define MOTOR_PIN 12
Servo motor;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Program begin...");
Serial.println("This program will calibrate the ESC.");
motor.attach(MOTOR_PIN);
Serial.println("Calibrating Maximum Signal");
Serial.println("Turn on power source, then wait 2 seconds and press any key + <enter>");
motor.writeMicroseconds(MAX_SIGNAL);
// Wait for input
while (!Serial.available());
Serial.read();
// Send min output
Serial.println("Calibrating Minimum Signal");
motor.writeMicroseconds(MIN_SIGNAL);
}
void loop() {
}