EO-Tools is a pure python toolbox that is currently able to search, download and process Sentinel-1 InSAR pairs, download and mosaic Sentinel-2 tiles and download various publicly available DEM (Digital Elevation Models). The S1 processor can compute phase, amplitude and coherence in the SAR geometry and reproject them in a geographic coordinate system. Example notebooks demonstrating the different features are located in the notebooks-cf folder of the github repository.
- Bursts from Sentinel-1 TOPS InSAR pairs can now be processed and combined without using SNAP.
- A new processor for IW subswath can be used -- see
s1-easy-tops-insar.ipynbin thenotebookfolder. - Bursts can also be processed individually using the
S1.coremodule for more flexibility. Results can be further processed as in-memory arrays or written as GeoTiff files. An example of such processing is found ins1-tops-core-demo.ipynb - More features/improvements will be added in the near future such as:
- Better memory and multi-core handling (probably using
dask) - Full product (all subswaths and polarization) processing with optional AOI selection
- Multi-temporal stacks
- Radiometric terrain correction
- Better memory and multi-core handling (probably using
- In a more distant future:
- Tools for change detection, polarimetry, speckle filtering, DEM generation
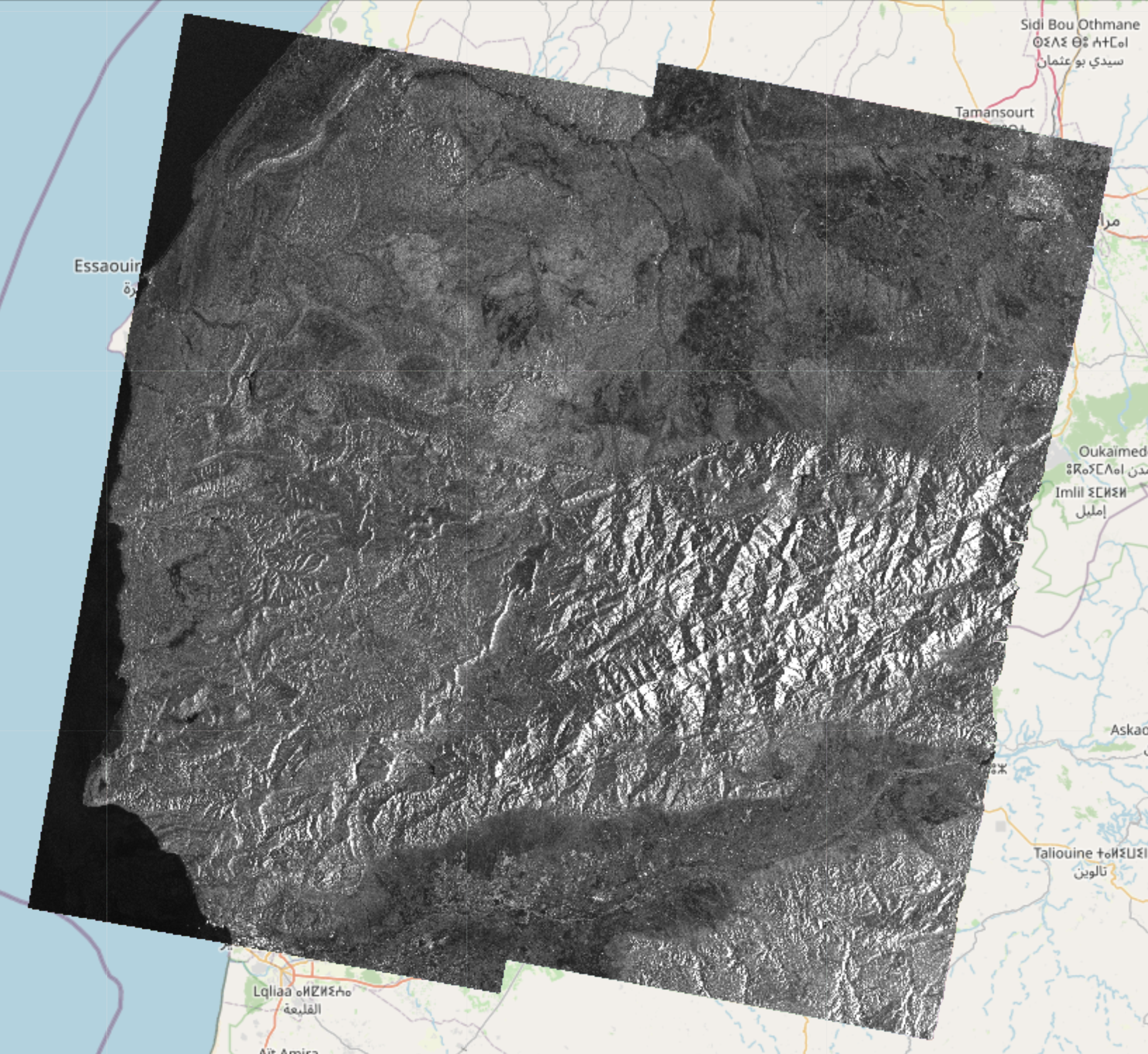
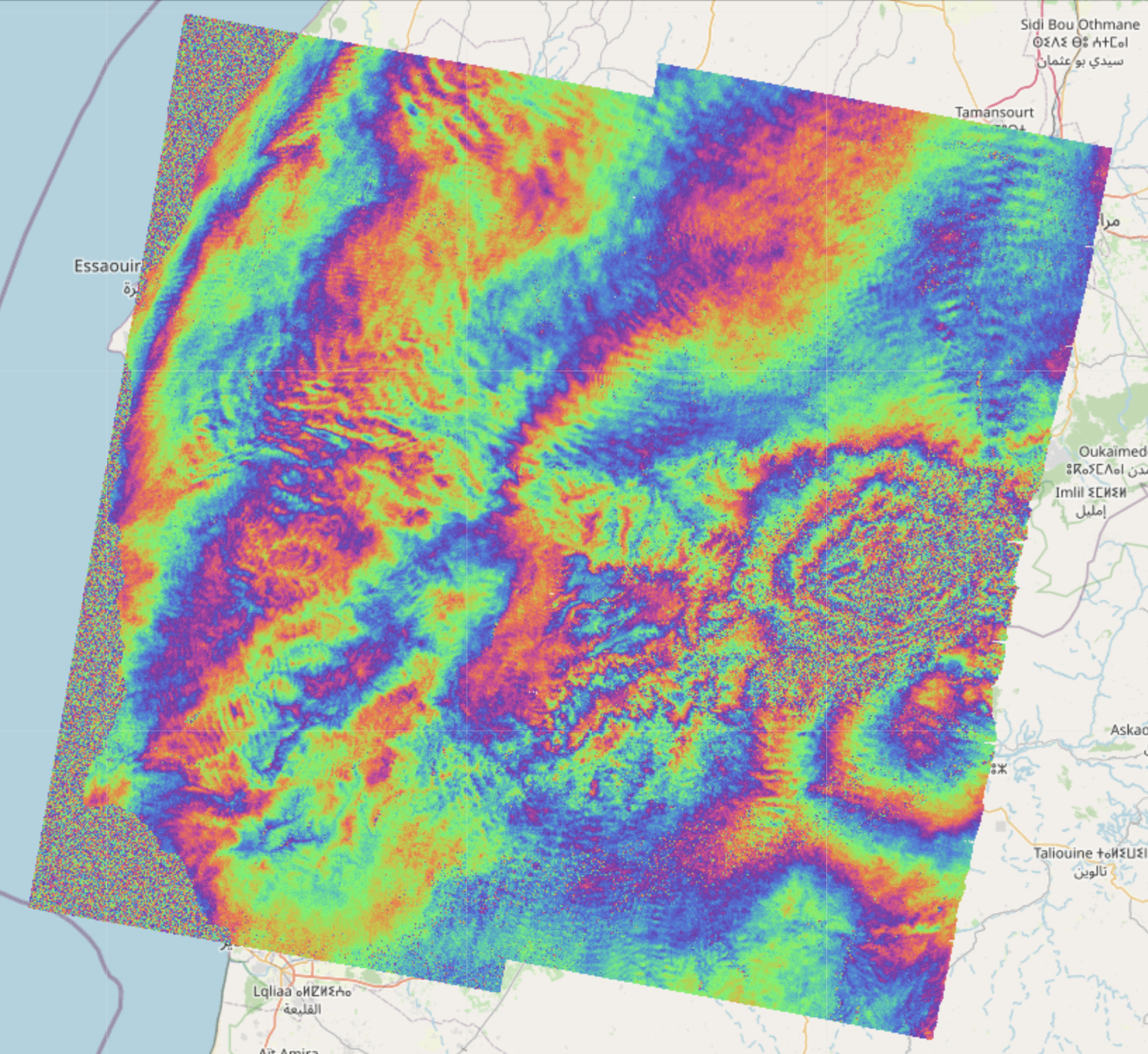
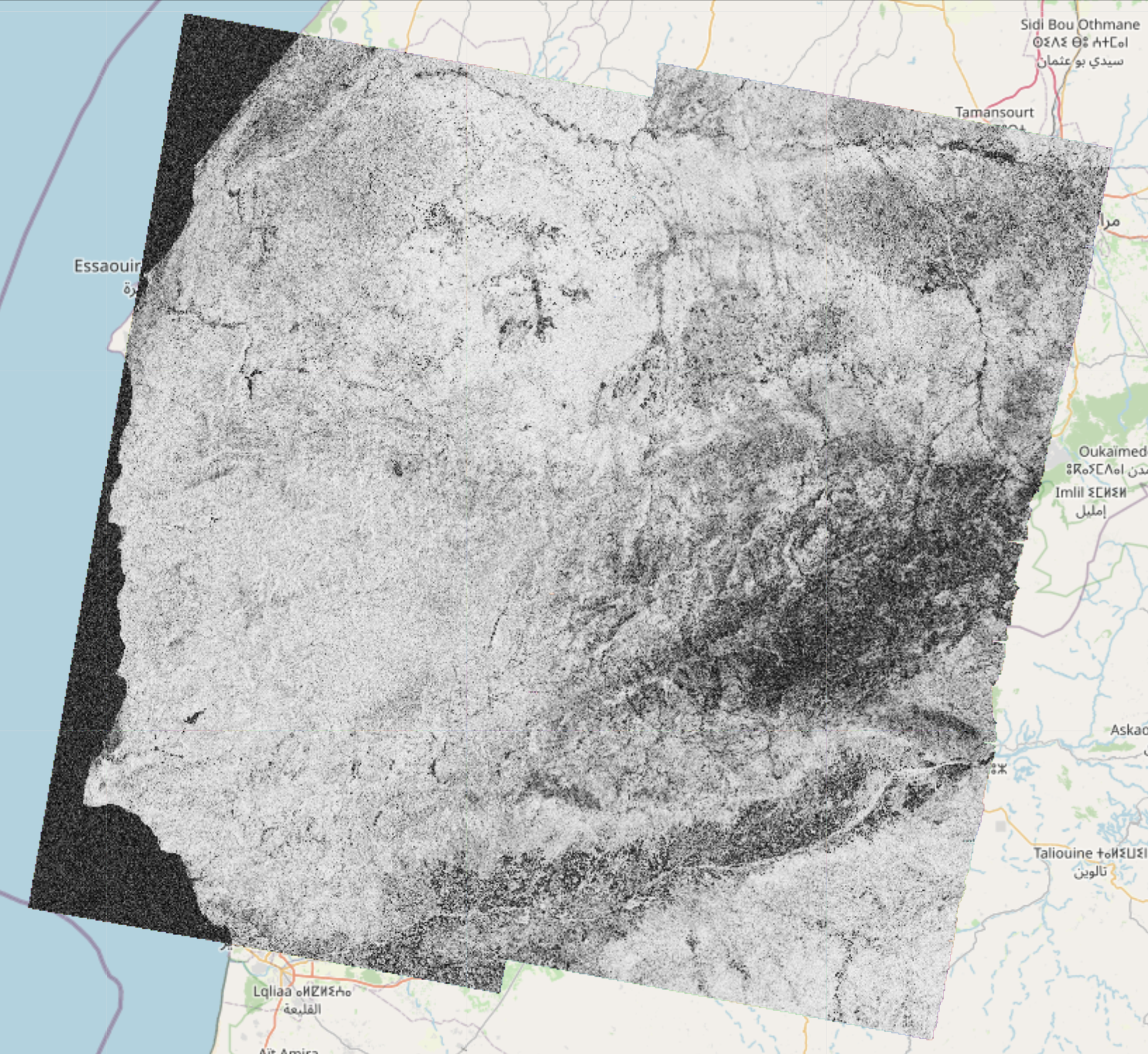
Here are examples of amplitude, phase and coherence computed using this framework:
- Because this project is in active development the API is likely to change.
- Currently, the available features are:
- Sentinel-1
- New standalone InSAR processor (see previous section)
- Legacy InSAR processor (running SNAP graphs through PyroSAR) computing the coherence, phase and intensities of an interferometric pair of SLC products
- Write the result as a geocoded (terrain corrected) COG (Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF) file
- Display these rasters on top of a folium map in a jupyter notebook
- Sentinel-2
- Tile merging and geocoding
- Write any band to COG files
- Visualization of color composites (Natural RGB, CIR, SWIR, etc) on a folium map
- DEM
- Automatically downloads and crops a DEM given a geometry
- All products
- Search catalog (using EODAG) and download products
- Explore products by displaying their footprint on a folium map (custom function)
- Show remote and local images on top of folium maps in the notebook
- Sentinel-1
- Example notebooks can be found in the
notebooks/folder
- The package comes in two flavors
- A conda package that contains the main functionality (Sentinel-1 InSAR, Sentinel-2 tile mosaic and DEM download)
- A docker version (for more advanced users) that additonally works with a TiTiler server for interactive visualization in the notebooks
- The legacy SNAP based processor is only available in the docker version.
- It is recommended to first create a conda environment to avoid package conflicts
- You need to have
condainstalled (ormamba/micromamba) - Then the package can be installed with these commands (replace
condabymambaormicromambaif needed):
conda env create -n eo_tools
conda activate eo_tools
conda install conda-forge::eo-tools - It works as a dev container for VSCode.
- Clone the github repository into the location of your choice.
- Volumes paths can (and should) be changed in
docker-compose.yml. - After opening the main directory, VSCode should detect the devcontainer file and ask to build the container. Once the container is running, the example notebooks in the
notebooksdirectory can be used.
- Alternatively, it should also be possible to start the container from the main directory with
docker-compose up -din a terminal and attach to the container with any editor supporting docker.
- Please make sure
jupyteris installed in your environment - Example jupyter notebooks demonstrate the different features
- For conda use the notebooks in the
notebooks-cfdirectory of the github repository - For docker use the notebooks in the
notebooksdirectory of the github repository
- This project was originally forked from: https://github.com/eo2cube/s1_processor/, however since 99% of the code is now original, I have detached the fork.
- Visualization functions are using TiTiler https://developmentseed.org/titiler/
- Product discovery and download are using EODAG https://github.com/CS-SI/eodag
- The old S1 processor uses pyroSAR https://github.com/johntruckenbrodt/pyroSAR which executes graphs with ESA's SNAP software https://github.com/senbox-org