The goal of this project is twofold:
- Allow FastApps users to obtain valuable insights from their data through an interactive chatbot
- In addition to the several software services that FastApps offers its customers, provide customers with an intra-company chat platform, much like Slack
This goal was achieved through the use of several AWS services, such as EC2, S3, CloudFormation, Lex, Lambda, and Route 53. Hence, it's beneficial to have basic knowledge about the aforementioned AWS services before attempting to understand the code in this project. An understanding of SAML authentication is also necessary, since SAML is used to authenticate users in this project.
The following is a brief, high-level explanation of what this project does when successfully run:
- Creates a MongoDB schema based on an existing template. The schema is filled with user specified values, and will be used by the new RocketChat instance to store data
- Creates a CloudFormation stack with a new EC2 instance, Route 53 DNS record pointing to the new EC2 instance and an S3 bucket for storing files that customers upload in the chat
- Runs a bash script on the new EC2 instance that installs Node.js, RocketChat, Docker, Apache, PM2 and a LetsEncrypt certificate for secure web communication (HTTPS)
- Downloads configuration files and scripts from S3, configures RocketChat with user specified settings, creates a proxy using Apache
- Starts RocketChat using PM2, runs a docker container that allows Hubot to respond to RocketChat messages. Hubot redirects user messages to either AWS Lex, or a Java Comprehend service.
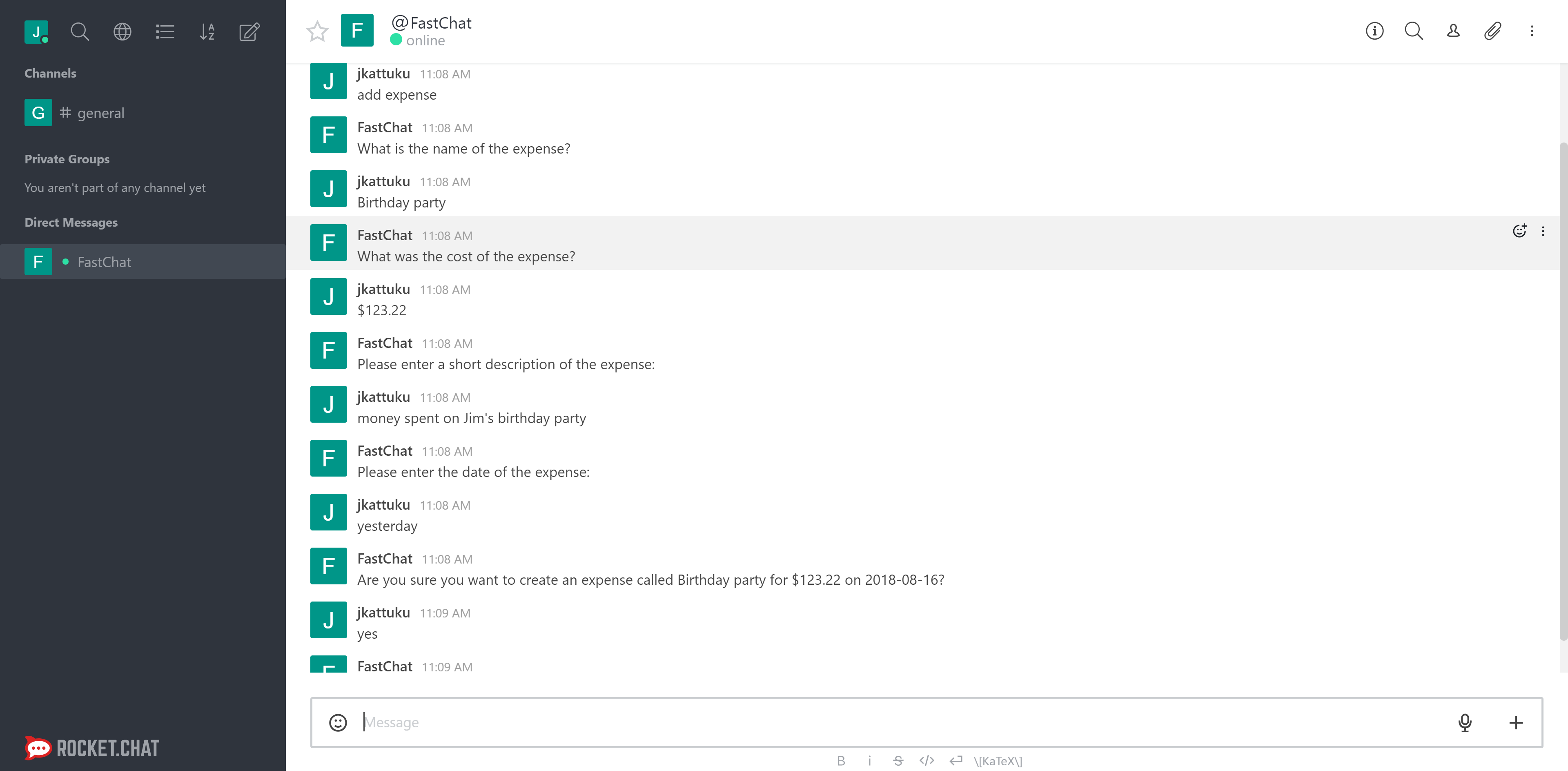
The result is a new RocketChat chat platform dedicated to the specified company. FastApps users withinin the company can sign in to the new RocketChat instance using their FastApps credentials, and can chat with each other through DMs or channels. Users can also communicate with a bot to ask questions regarding their data, or perform certain actions. Currently, the only supported action is "Add Expense" which adds an expense for the user. The screenshot below shows the conversation flow between a user and the bot for the "Add Expense" action.
-
Place the following files in a publically accessible bucket in AWS S3:
HubotScript.js,rocketChat.conf,RocketChatServerConfig.json. The files themselves MUST also be made public when uploaded to the bucket. If either the files or the bucket are not publically accessible, the API will fail to fetch them during EC2 instance creation, causing errors. After these files have been uploaded to S3, note the URLs of each of these files. URLs for files in S3 are of the following form: https://{bucketName}.s3.amazonaws.com/{path-to-file}. Replace the follwing parameters in thecreateRocketChatServer.jsfile with the values you noted down:hubotScriptS3URL- replace with S3 URL ofHubotScript.jstemplateURL- replace with S3 URL ofRocketChatServerConfig.jsonapacheConfigURL- replace with S3 URL ofrocketChat.conf
-
Create a role (if it does not already exist) in AWS with the following permission policies attached to it:
AmazonS3FullAccess,AmazonLexRunBotsOnly. Note down the name of the role you created, and replace theroleNameparameter in thecreateRocketChatServer.jsfile with the role name. This role allows each EC2 instance to communicate with Amazon Lex, and upload files to S3. -
Create an EC2 security group (if it doesn't already exist) that has ports 80 and 443 open. You can, optionally, open port 22 to enable SSH access to the server, but this should be done with caution. Note the name of the security group and replace the
securityGroupparameter in thecreateRocketChatServer.jsfile with this name. -
For the chat bot to properly function, Amazon Lex and Amazon Lambda must be properly configured. In Lex, there must be a bot (usually called 'FastChat') with an intent called 'AddExpense'. There are 2 Lambda functions that should be attached to this bot:
AddExpenseVerificationfor the verification of input, andAddExpenseFulfillmentfor the fulfillment of the intent. The Lambda functions can be made using the ZIP files in the "Lambda Functions" folder (AddExpenseFulfillment.zipandAddExpenseVerification.zip). IMPORTANT - if the name of the bot is not "FastChat", thebotNameand thebotAliasproperties in theHubotScript.jsfile must be modified. -
The remaining parameters in the
createMongoSchema.jsandcreateRocketChatServer.jsfiles must be changed depending on the setup. For more information on these parameters, refer to the "Important Files" section below. -
Put
createMongoSchema.jsandcreateRocketChatServer.jsin an environment with Node.js installed (Node version >= 8). More information on these two files can be found below in the "Important Files" section. These files can be run with the following commands:
node createMongoSchema.js
node createRocketChatServer.jsNOTE: the createMongoSchema.js file must be run before the createRocketChatServer file, since the mongo schema must be created before the RocketChat instance can start running. RocketChat stores data in MongoDB, so the schema must exist for RocketChat to connect to it.
- Copies a Rocket Chat template schema in MongoDB, and fills in certain values based on user input (Ex: schema name, site URL, SAML settings)
- The copied schema, after being filled with the appropriate values, will be used by the new RocketChat instance for storing data
mongodb- node module used for connecting to and querying mongo databaseassert- node module used for unit tests and assertions
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
mongoURL |
The URL of the Mongo database which should be copied from. This URL should be of the following format: mongodb://{mongo-domain}:27017/{schema-to-be-copied-from} |
copyFrom |
The name of the Mongo schema to be copied. It is usually "rocketChatTemplate" |
scdp |
SAML Custom Default Provider - this parameter changes the location of the metadata file for RocketChat. The location of this file is of the following format: https://{rocketchat-domain}/_saml/metadata/{scdp} |
scdep |
SAML Custom Default Entry Point - The URL provided by the SAML IDP for logging in. The format of this URL is: https://{saml-domain}/simplesaml/saml2/idp/SSOService.php |
scdisru |
SAML Custom Default IDP Single Log Out Redirect URL - the URL provided by the idp for logging out. The format of this URL is: https://{saml-domain}/simplesaml/saml2/idp/SingleLogoutService.php |
hostedZone |
The name of the AWS Route 53 hosted zone in which the DNS record will be created |
region |
The value of this parameter MUST be "us-east-1". Since S3 is a regionless service, the default region that is used when communicating via API is "us-east-1" |
This file uses a CloudFormation Template (RocketChatServerConfig.json) to create a new EC2 instance, a Route 53 DNS record and a S3 bucket for file uploads. It uses the AWS SDK for Node.js to create the stack.
aws-sdk- node module for interacting with AWS API
Detailed descriptions of the parameters for this function can be found in the createRocketChatServer.js file. There are many important parameters in this file that MUST be set correctly for this function to work, so take the time to read through the descriptions of the parameters and set them accordingly.
There are two important parameters in the createRocketChatServer.js file: accessKeyId and secretAccessKey. These are AWS credentials that are used to create the CloudFormation stack, which consists of an EC2 instance, a Route 53 DNS record, and an S3 bucket. Hence, the user whose credentials are being used MUST have permission to create and modify the aforementioned AWS resources.
This JSON file is a CloudFormation template that specifies the architecture configuration to be created when stack creation is initiated. This template also contains the bash script that is run on the new EC2 instance at launch.
Important - the parameters specified in the CloudFormation template must match the parameters specified in the Parameters array of the params variable in the createRocketChatServer.js file. In other words, if a parameter is added to the createRocketChatServer.js file and the parameter needs to be passed into the CloudFormation template, the parameter must also be added to the CloudFormation template.
This file is a script for Hubot, which is used to redirect the conversation flow of the chatbot. Essentially, Hubot receives all messages that the user enters, and it classifies the user input as a question or an action. Input is classified as a question if it begins with "who", "what", "where", "when", "why" or "how". All other inputs are classified as actions. If the input is flagged as a question, it is sent to a Java service that uses AWS Comprehend to reply to the question. If the question is flagged as an action, it is sent to AWS Lex, which interprets the input and tries to match it to an intent. Currently, the only developed intent is the "AddExpense" intent, but it's easy to imitate the setup for this intent and modify it to create new intents.
aws-sdk- node module for interacting with AWS API. No need to install this module, since this is taken care of in the bash script.