The Descope SDK for React provides convenient access to the Descope for an application written on top of React. You can read more on the Descope Website.
- The SDK supports React version 16 and above.
- A Descope
Project IDis required for using the SDK. Find it on the project page in the Descope Console.
Install the package with:
npm i --save @descope/react-sdkimport { AuthProvider } from '@descope/react-sdk';
const AppRoot = () => {
return (
<AuthProvider
projectId="my-project-id"
// If the Descope project manages the token response in cookies, a custom domain
// must be configured (e.g., https://auth.app.example.com)
// and should be set as the baseUrl property.
// baseUrl = "https://auth.app.example.com"
>
<App />
</AuthProvider>
);
};You can use default flows or provide flow id directly to the Descope component
import { SignInFlow } from '@descope/react-sdk'
// you can choose flow to run from the following
// import { SignUpFlow } from '@descope/react-sdk'
// import { SignUpOrInFlow } from '@descope/react-sdk'
const App = () => {
return (
{...}
<SignInFlow
onSuccess={(e) => console.log('Logged in!')}
onError={(e) => console.log('Could not logged in!')}
/>
)
}import { Descope } from '@descope/react-sdk'
const App = () => {
return (
{...}
<Descope
flowId="my-flow-id"
onSuccess={(e) => console.log('Logged in!')}
onError={(e) => console.log('Could not logged in')}
// onReady={() => {
// This event is triggered when the flow is ready to be displayed
// Its useful for showing a loading indication before the page ready
// console.log('Flow is ready');
// }}
// theme can be "light", "dark" or "os", which auto select a theme based on the OS theme. Default is "light"
// theme="dark"
// locale can be any supported locale which the flow's screen translated to, if not provided, the locale is taken from the browser's locale.
// locale="en"
// debug can be set to true to enable debug mode
// debug={true}
// tenant ID for SSO (SAML) login. If not provided, Descope will use the domain of available email to choose the tenant
// tenant=<tenantId>
// Redirect URL for OAuth and SSO (will be used when redirecting back from the OAuth provider / IdP), or for "Magic Link" and "Enchanted Link" (will be used as a link in the message sent to the the user)
// redirectUrl=<redirectUrl>
// autoFocus can be true, false or "skipFirstScreen". Default is true.
// - true: automatically focus on the first input of each screen
// - false: do not automatically focus on screen's inputs
// - "skipFirstScreen": automatically focus on the first input of each screen, except first screen
// autoFocus="skipFirstScreen"
// errorTransformer is a function that receives an error object and returns a string. The returned string will be displayed to the user.
// NOTE: errorTransformer is not required. If not provided, the error object will be displayed as is.
// Example:
// const errorTransformer = useCallback(
// (error: { text: string; type: string }) => {
// const translationMap = {
// SAMLStartFailed: 'Failed to start SAML flow'
// };
// return translationMap[error.type] || error.text;
// },
// []
// );
// ...
// errorTransformer={errorTransformer}
// ...
// form is an object the initial form context that is used in screens inputs in the flow execution.
// Used to inject predefined input values on flow start such as custom inputs, custom attributes and other inputs.
// Keys passed can be accessed in flows actions, conditions and screens prefixed with "form.".
// NOTE: form is not required. If not provided, 'form' context key will be empty before user input.
// Example:
// ...
// form={{ email: "[email protected]", firstName: "test", "customAttribute.test": "aaaa", "myCustomInput": 12 }}
// ...
// client is an object the initial client context in the flow execution.
// Keys passed can be accessed in flows actions and conditions prefixed with "client.".
// NOTE: client is not required. If not provided, context key will be empty.
// Example:
// ...
// client={{ version: "1.2.0" }}
// ...
// logger is an object describing how to log info, warn and errors.
// NOTE: logger is not required. If not provided, the logs will be printed to the console.
// Example:
// const logger = {
// info: (title: string, description: string, state: any) => {
// console.log(title, description, JSON.stringify(state));
// },
// warn: (title: string, description: string) => {
// console.warn(title);
// },
// error: (title: string, description: string) => {
// console.error('OH NOO');
// },
// }
// ...
// logger={logger}
// ...
/>
)
}Use the useDescope, useSession and useUser hooks in your components in order to get authentication state, user details and utilities
This can be helpful to implement application-specific logic. Examples:
- Render different components if current session is authenticated
- Render user's content
- Logout button
import { useDescope, useSession, useUser } from '@descope/react-sdk';
import { useCallback } from 'react';
const App = () => {
// NOTE - `useDescope`, `useSession`, `useUser` should be used inside `AuthProvider` context,
// and will throw an exception if this requirement is not met
// useSession retrieves authentication state, session loading status, and session token
const { isAuthenticated, isSessionLoading, sessionToken } = useSession();
// useUser retrieves the logged in user information
const { user } = useUser();
// useDescope retrieves Descope SDK for further operations related to authentication
// such as logout
const sdk = useDescope();
if (isSessionLoading || isUserLoading) {
return <p>Loading...</p>;
}
const handleLogout = useCallback(() => {
sdk.logout();
}, [sdk]);
if (isAuthenticated) {
return (
<>
<p>Hello {user.name}</p>
<button onClick={handleLogout}>Logout</button>
</>
);
}
return <p>You are not logged in</p>;
};Note: useSession triggers a single request to the Descope backend to attempt to refresh the session. If you don't useSession on your app, the session will not be refreshed automatically. If your app does not require useSession, you can trigger the refresh manually by calling refresh from useDescope hook. Example:
const { refresh } = useDescope();
useEffect(() => {
refresh();
}, [refresh]);For more SDK usage examples refer to docs
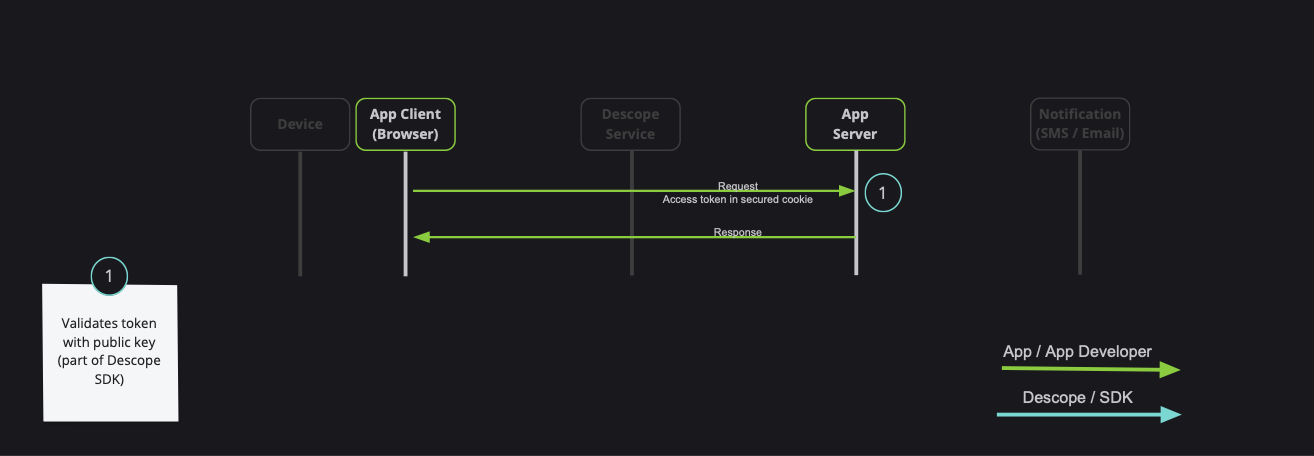
When developing a full-stack application, it is common to have private server API which requires a valid session token:
Note: Descope also provides server-side SDKs in various languages (NodeJS, Go, Python, etc). Descope's server SDKs have out-of-the-box session validation API that supports the options described bellow. To read more about session validation, Read this section in Descope documentation.
There are 2 ways to achieve that:
- Using
getSessionTokento get the token, and pass it on theAuthorizationHeader (Recommended) - Passing
sessionTokenViaCookieboolean prop to theAuthProvidercomponent (Use cautiously, session token may grow, especially in cases of using authorization, or adding custom claim)
An example for api function, and passing the token on the Authorization header:
import { getSessionToken } from '@descope/react-sdk';
// fetch data using back
// Note: Descope backend SDKs support extracting session token from the Authorization header
export const fetchData = async () => {
const sessionToken = getSessionToken();
const res = await fetch('/path/to/server/api', {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${sessionToken}`
}
});
// ... use res
};An example for component that uses fetchData function from above
// Component code
import { fetchData } from 'path/to/api/file'
import { useCallback } from 'react'
const Component = () => {
const onClick = useCallback(() => {
fetchData()
},[])
return (
{...}
{
// button that triggers an API that may use session token
<button onClick={onClick}>Click Me</button>
}
)
}Passing sessionTokenViaCookie prop to AuthProvider component. Descope SDK will automatically store session token on the DS cookie.
Note: Use this option if session token will stay small (less than 1k). Session token can grow, especially in cases of using authorization, or adding custom claims
Example:
import { AuthProvider } from '@descope/react-sdk';
const AppRoot = () => {
return (
<AuthProvider projectId="my-project-id" sessionTokenViaCookie>
<App />
</AuthProvider>
);
};Now, whenever you call fetch, the cookie will automatically be sent with the request. Descope backend SDKs also support extracting the token from the DS cookie.
Note:
The session token cookie is set as a Secure cookie. It will be sent only over HTTPS connections.
In addition, some browsers (e.g. Safari) may not store Secure cookie if the hosted page is running on an HTTP protocol.
You can also use the following functions to assist with various actions managing your JWT.
getSessionToken() - Get current session token.
getRefreshToken() - Get current refresh token.
refresh(token = getRefreshToken()) - Force a refresh on current session token using an existing valid refresh token.
isSessionTokenExpired(token = getSessionToken()) - Check whether the current session token is expired. Provide a session token if is not persisted (see token persistence).
isRefreshTokenExpired(token = getRefreshToken()) - Check whether the current refresh token is expired. Provide a refresh token if is not persisted (see token persistence).
getJwtRoles(token = getSessionToken(), tenant = '') - Get current roles from an existing session token. Provide tenant id for specific tenant roles.
getJwtPermissions(token = getSessionToken(), tenant = '') - Fet current permissions from an existing session token. Provide tenant id for specific tenant permissions.
Descope SDK is automatically refreshes the session token when it is about to expire. This is done in the background using the refresh token, without any additional configuration.
If the Descope project settings are configured to manage tokens in cookies.
you must also configure a custom domain, and set it as the baseUrl prop in the AuthProvider component. See the above AuthProvider usage for usage example.
Descope stores two tokens: the session token and the refresh token.
- The refresh token is either stored in local storage or an
httpOnlycookie. This is configurable in the Descope console. - The session token is stored in either local storage or a JS cookie. This behavior is configurable via the
sessionTokenViaCookieprop in theAuthProvidercomponent.
However, for security reasons, you may choose not to store tokens in the browser. In this case, you can pass persistTokens={false} to the AuthProvider component. This prevents the SDK from storing the tokens in the browser.
Notes:
- You must configure the refresh token to be stored in an
httpOnlycookie in the Descope console. Otherwise, the refresh token will not be stored, and when the page is refreshed, the user will be logged out. - You can still retrieve the session token using the
useSessionhook.
Descope stores the last user information in local storage. If you wish to disable this feature, you can pass storeLastAuthenticatedUser={false} to the AuthProvider component. Please note that some features related to the last authenticated user may not function as expected if this behavior is disabled.
Widgets are components that allow you to expose management features for tenant-based implementation. In certain scenarios, your customers may require the capability to perform managerial actions independently, alleviating the necessity to contact you. Widgets serve as a feature enabling you to delegate these capabilities to your customers in a modular manner.
Important Note:
- For the user to be able to use the widget, they need to be assigned the
Tenant AdminRole.
The UserManagement widget lets you embed a user table in your site to view and take action.
The widget lets you:
- Create a new user
- Edit an existing user
- Activate / disable an existing user
- Reset an existing user's password
- Remove an existing user's passkey
- Delete an existing user
Note:
- Custom fields also appear in the table.
import { UserManagement } from '@descope/react-sdk';
...
<UserManagement
widgetId="user-management-widget"
tenant="tenant-id"
/>Example: Manage Users
The RoleManagement widget lets you embed a role table in your site to view and take action.
The widget lets you:
- Create a new role
- Change an existing role's fields
- Delete an existing role
Note:
- The
Editablefield is determined by the user's access to the role - meaning that project-level roles are not editable by tenant level users. - You need to pre-define the permissions that the user can use, which are not editable in the widget.
import { RoleManagement } from '@descope/react-sdk';
...
<RoleManagement
widgetId="role-management-widget"
tenant="tenant-id"
/>Example: Manage Roles
The AccessKeyManagement widget lets you embed an access key table in your site to view and take action.
The widget lets you:
- Create a new access key
- Activate / deactivate an existing access key
- Delete an exising access key
import { AccessKeyManagement } from '@descope/react-sdk';
...
{
/* admin view: manage all tenant users' access keys */
}
<AccessKeyManagement
widgetId="access-key-management-widget"
tenant="tenant-id"
/>
{
/* user view: mange access key for the logged-in tenant's user */
}
<AccessKeyManagement
widgetId="user-access-key-management-widget"
tenant="tenant-id"
/>Example: Manage Access Keys
The AuditManagement widget lets you embed an audit table in your site.
import { AuditManagement } from '@descope/react-sdk';
...
<AuditManagement
widgetId="audit-management-widget"
tenant="tenant-id"
/>Example: Manage Audit
The UserProfile widget lets you embed a user profile component in your app and let the logged in user update his profile.
The widget lets you:
- Update user profile picture
- Update user personal information
- Update authentication methods
- Logout
import { UserProfile } from '@descope/react-sdk';
...
<UserProfile
widgetId="user-profile-widget"
onLogout={() => {
// add here you own logout callback
window.location.href = '/login';
}}
/>Example: User Profile
You can find an example react app in the examples folder.
To run the examples, set your Project ID by setting the DESCOPE_PROJECT_ID env var or directly
in the sample code.
Find your Project ID in the Descope console.
export DESCOPE_PROJECT_ID=<Project-ID>Alternatively, put the environment variable in .env file in the project root directory.
See bellow for an .env file template with more information.
Run the following command in the root of the project to build and run the example:
npm i && npm startSee the following table for customization environment variables for the example app:
| Env Variable | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| DESCOPE_FLOW_ID | Which flow ID to use in the login page | sign-up-or-in |
| DESCOPE_BASE_URL | Custom Descope base URL | None |
| DESCOPE_THEME | Flow theme | None |
| DESCOPE_LOCALE | Flow locale | Browser's locale |
| DESCOPE_REDIRECT_URL | Flow redirect URL for OAuth/SSO/Magic Link/Enchanted Link | None |
| DESCOPE_TENANT_ID | Flow tenant ID for SSO/SAML | None |
| DESCOPE_DEBUG_MODE | "true" - Enable debugger "false" - Disable flow debugger |
None |
| DESCOPE_STEP_UP_FLOW_ID | Step up flow ID to show to logged in user (via button). e.g. "step-up". Button will be hidden if not provided | None |
| DESCOPE_TELEMETRY_KEY | String - Telemetry public key provided by Descope Inc | None |
Example for .env file template:
# Your project ID
DESCOPE_PROJECT_ID="<Project-ID>"
# Login flow ID
DESCOPE_FLOW_ID=""
# Descope base URL
DESCOPE_BASE_URL=""
# Set flow theme to dark
DESCOPE_THEME=dark
# Set flow locale, default is browser's locale
DESCOPE_LOCALE=""
# Flow Redirect URL
DESCOPE_REDIRECT_URL=""
# Tenant ID
DESCOPE_TENANT_ID=""
# Enable debugger
DESCOPE_DEBUG_MODE=true
# Show step-up flow for logged in user
DESCOPE_STEP_UP_FLOW_ID=step-up
# Telemetry key
DESCOPE_TELEMETRY_KEY=""
The Descope SDK caches the user and session token in the frontend. If you update the user in your backend (using Descope Management SDK/API for example), you can call me / refresh from useDescope hook to refresh the user and session token. Example:
const sdk = useDescope();
const handleUpdateUser = useCallback(() => {
myBackendUpdateUser().then(() => {
sdk.me();
// or
sdk.refresh();
});
}, [sdk]);To learn more please see the Descope Documentation and API reference page.
If you need help you can email Descope Support
The Descope SDK for React is licensed for use under the terms and conditions of the MIT license Agreement.