Informatica is a company which offers data integration tool know as Informatica based on ETL architecture. It provides data integration software and services for various businesses, industries and government organizations including telecommunication, health care, financial and insurance services. When we say Informatica, it refers to the Informatica PowerCenter tool for ETL.
The latest version of Informatica PowerCenter available is 10.5.2, The different editions for the PowerCenter are
- Standard edition
- Advanced edition
- Premium edition
The popular clients using Informatica Power center as a data integration tool are U.S Air Force, Allianz, Fannie Mae, ING, Samsung, etc. The popular tools available in the market in competition to Informatica are IBM Datastage, Oracle OWB, Microsoft SSIS and Ab Initio.
Data validation is the practice of checking the integrity, accuracy and structure of data before it is used for a business operation. Business operation can be like ETL jobs.
Data integration is the process of combining data from different sources into a single, unified view. Integration begins with the ingestion process, and includes steps such as cleansing, ETL mapping, and transformation. Data integration ultimately enables analytics tools to produce effective, actionable business intelligence. For example , you can connect to an SQL Server Database or Oracle Database or flat files(2d files) or excel all of them can be integrateg and the data is stored into a third system like a data warehouse.
Data ingestion is the process of transporting data from one or more sources to a target site for further processing and analysis.
Informatica is a company that offers data integration products for ETL, data masking, data Quality, data replica, data virtualization, master data management, etc. Informatica ETL is the most commonly used Data integration tool used for connecting & fetching data from different data sources.
Some of the typical use cases for approaching this software are:
- An organization migrating from an existing software system to a new database system.
- To set up a Data Warehouse in an organization where the data is moved from the Production/ data gathering system to Warehouse.
- It serves as a data cleansing tool where data is detected, corrected, or removed from corrupt or inaccurate records from a database.
-
Extract: The data is extracted from different sources of data. Common data-source formats include relational databases, XML and flat files, Information Management System (IMS) or other data structures. An instant data validation is performed to confirm whether the data pulled from the sources have the correct values in a given domain.
-
Transform: A set of rules or logical functions like cleaning of data are applied to the extracted data in order to prepare it for loading into a target data source. Cleaning of data implies passing only the "proper" data into the target source. There are many transformation types that can be applied to data as per the business need. Some of them can be column or row-based, coded and calculated values, key-based, joining different data sources, etc.
-
Load: The data is simply loaded into the target data source.
Informatica comes to the picture wherever we have a data system available and at the backend we want to perform certain operations on the data. It can be like cleaning up of data, modifying the data, etc. based on certain set of rules or simply loading of bulk data from one system to another.
-
Data Mart-: Multiple Data Source => Data Warehouse => split(Sales,Product). So, usuallt data mart is project specified.
-
Informatica client we have designer, workflow manager, workflow monitor and monitor.
-
Informatica server side we have Repository service, integration service, Domain, and Node.
-
Designer we can import source, target and create mapping(ETL jobs)
-
Whatever logic written in designer phase transfered to workflow. So, basically it create a task.
-
Monitor
- Gantt chart - Explanation via lines.
- Task view - Names + Completion time.
-
So when we execute source table consisting some data on Informatica side then transformation will run and output data will be shown on screen.
-
Mapping naming convention "m_databasename"
-
Expression transformation convention "exp_dataname"
-
Session convention in workflow "s_...."
-
Workflow convention "wf_...."
-
Informatica take data types from source like oracle(Int) and convert it into it's compaitable data type like decimal.
-
F(X) expression transformation.
-
So, usually we extract data from source after that applied certain transformation and load it somewhere ETL.
-
Arrange all iconic to get symbolic view.
- The Informatica domain is the fundamental administrative unit.
- The Informatica domain consists of nodes and services. These nodes and services are categorized into folders or sub-folders based on administration requirements and design architecture.
- The Console web page of the Informatica administrator creates a domain that looks like a folder. Inside this folder, we can create a node with the services.
- In the Informatica domain, a node is a logical representation of the machine. All the services and processes run inside the domain in the Informatica. Multiple nodes can be present in a single domain. A gateway node receives the request from the clients and guides them to their respective services.
- The domain provides two types of services, such as:
- Service Manager: It manages domain operations such as logging, authentication, and authorization. It runs the application services on the nodes and leads users and groups.
- Application Services: It represents the server-specific services such as repository services, reporting services, and integration services. The application service can run on different nodes based on configuration.
- Informatica Tranformation Link
-
R-> Repository
-
D-> Design
-
M-> Mapping
-
W-> Workflow where we compile
-
Edit transformation we have input port, output port, variable port, and rank port.
-
Processes involved in Informatica
- Setting up source in the Informatica Designer. If it coming from a Oracle DB or something which has standardized datatypes you don't need to chaAdd nge the Prec, else you need to set them up to normal standard values.
- Setting up target in the Informatica Designer
-
<--Creating Mappings--> It also is created inside Informatica Designer Mapping Window.
- Naming convention for any mapping is as follows m_WHATEVERYOUARE DOING.
- When you drag the source a source qualifier comes along with it and it is there in place cause informatica converts the datatypes into compatible datatypes in informatica.
- Add the transformation layer into the mappings and drag all the source input columns into it. Add appropriate transformations and move to next step.
- Load the data into the target.
-
<--Creating Workflow-->
- Create Task -> Create Session (NC: s_WHATEVERYOUWANT), select the appropriate mapping.
- Go to workflow -> Create a new workflow (NC: wf_WHATEVERYOUWANT) -> Drag the appropriate sessions -> Use linkers to connect the start with sessions.
- In the linked workflow, select the session and added source file details will be available in the details and update the connections/properties according to your requirements.
- Execute the workflow.
-
Session -: A session is a set of instructions that tells the Integration Service how to move data from sources to targets. A session is a task, similar to other tasks available in the Workflow Manager. You create a session for each mapping that you want the Integration Service to run.
-
Expression Transformation (NC: exp_COMBINING_FNAME_LNAME) You can add, copy, delete ports, change properties, apply SQL functions on the columns.
| Router Transformation | Filter Transformation |
|---|---|
| We can specify multiple filter condition | We can specify only one filter condition |
| Active Transformation | Active Transformation |
| We have option to save the records which do not satisfy the filter conditions. | We don't have option to save the records which do not satisfy the filter conditions. |
| Similar to if condition | Similar as where clause in SQL |
-
Router Transformation (NC: rtr_WHATEVERYOUWANT) Source --> Source Qualifier --> Router --> Target Multiple sets of output data based upon multiple filter conditions and a default group which does not satisfy any of the above filter criteria.
-
Filter Transformation -: It filters the record based on the condition given in the filter. Router faster than filter transformation.
-
Aggregator Transformation -: Is an active transformation is used to perform aggregate calculations like sum, average, etc. The integration service stores the data group and row data in aggregate cache. Can't use variable ports in here.
-
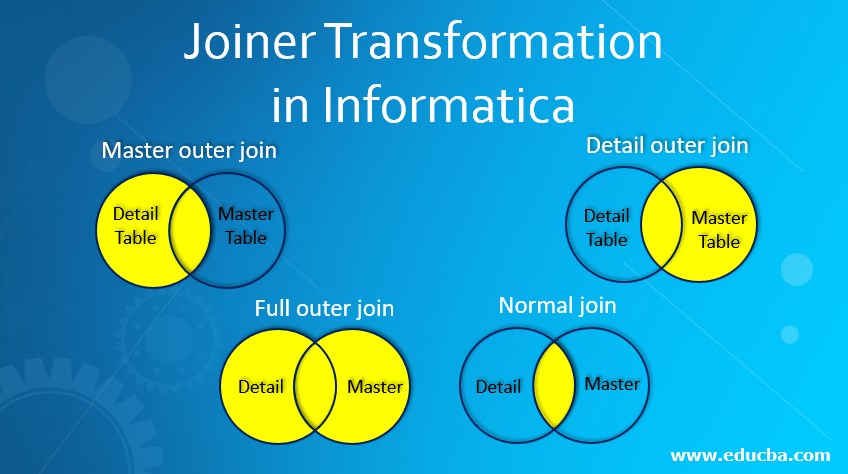
Joiner Transformation -: It is an active transformation and connected transformation that provides you the option to create joins in informatica, the joins created using joiner transformation are similar to the joins in databases. The ad of jt is thatjoins can be created for heterogeneous systems. In jt, there are two sources --> master source and detail source. So, the source table which has more number of record will be considered as detail source. Master source have less number of record. Master is same as ram or cache we can't put everything in it. So, usually we declare source table as the master source. Prefix is jnr_convention. for example -: Subject Table(Master consisit of sub_id and sub_name) and Student Table(Details consist of stud_name and sub_id)
| Informatica | DB |
|---|---|
| Master Outer Join(Detail source + master source matching column) | Right Outer Join |
| Detail Outer Join(Master source + detail source matching column) | Left Outer Join |
| Full Outer Join | Full Outer Join |
| Normal Join | Inner Join |
-
Rank Transformation -: It is an active and connected transformation, it is used to select the top or bottom rank of data. It is used to select the smallest/largest numeric/string values. The integration service caches the input data and then performs rank calculation. Represent in rnk_name.
-
Sequence Transformation -: It is a generator transformation and is passive so it does not affect the number of input rows. The generator is used to generate PK values and it's used to generate numeric sequences values like 1,2,3,4,5 etc. 2 components CURR_VAL, NEXT_VAL. In sequence tranformation we have following which is given below.
- Start Value(First value generated by transformation, default value can be 0)
- Incremented by(Default increment is 1)
- End value(Max value)
- Cycle(after reaching last it can again start from the beggining)
-
Lookup Transformation -: It is a passive transformation used to look up a source, source qualifier, or target to get the relevant data. It's a kind of join operation in which one of the joining tables is the source data, and the other joining table is the lookup table. Two types of lookup: relational (lookup table from DB table), flat-file(any sort of file), cached/un cached, connected/unconnected. Eg-: Employee(which has source table consist of(Emp_Id, Emp_Name,Dept_Id)) + Department(Lookup Table(Dept_Id,Dept_Name)) = Employee_Dept(Target(Emp_Id,Emp_Name,Dept_id,Dept_Name)). Lookup table classified in 3 types-:
- Relational or flat file-: We use relational table as lookup source. So, in above example department is our relational lookup.
- Cached or un cached-: By default lookup is cached. Cached lookup is where data is stored in memory temporarily. When directly processed without storing somewhere then it's un cached.
- Connected or Unconnected-:
Connected Unconnected Received input directly from the pipeline Received input from the result of LKP Dynamic + Static Cache Static Cache(Data not change) To identify when input is coming and output is there A individual table
-
Union Transformation-: It's use to combine data from multiple sources like flat files, sql table an produce one output to store in target table. It's active transformation and it's similar to SQL UNION ALL.
-
Normalization transformation-: It's active transformation. It is use to transpose the data in columns to rows. Similar to Normalization. Naming convention nrm_abc.
- GCID - General column ID. It's act as a index of general occuring data.
- GK_Value - It increase the sequence of each input row.
-
Update strategy transformation - It is use to handle insert, update and, delete operation. Whenever we are inserting something inside the target table we must know what we are entering. It is only applicable if there is primary key in target table. If there is no primary ket then we need to specifiy primary key in target defination. example-: we have target employee table and source employee table which mapping is already created. In source emp no 2 shifted to some new department so the update must be done on target table.
- DD_Insert(numberic value 0)
- DD_Update(1)
- DD_Delete(2)
- DD_Reject(3)
-
Store proc transformation-: it is use to execute stored procs through informatica ETL. It is use to perform some complex calculations. Check the status of target db before loading data into it. Determine if enough space exists in db. Two types of stored procs-:
- Connected -: Connected with other transformation.
- Unconnected -: Is the one which is not connected to other transformation.
Stored Procedure Transformation in Informatica is a passive transformation and can be used in both connected and unconnected mode. The stored procedures are stored and run within the database and it also contains a pre-compiled collection of PL-SQL statements.
-
Inserting data into a table: A stored procedure can be used to insert data into a table, validate the data before it is inserted, and handle any errors that occur.
-
Updating data in a table: A stored procedure can be used to update existing data in a table, validate the new data before it is updated, and handle any errors that occur.
-
Deleting data from a table: A stored procedure can be used to delete data from a table, validate the data before it is deleted, and handle any errors that occur.
-
Slowly changing dimensions-: At some time we are not sure when the new update or insert operation arrives. So, to handle all that stuff's we need SCD. usually, data changes occur slowly rather regularly.
-
Mapplet -: An Informatica Mapplet is a reusable object that comprises a set of transformations that can be used in multiple maps. Mapping is developed with different transformation but not reusable. Mapplet can be reused other mapping and also mapplet. Mapping is developed for what data move to target, what modification done upon that. Mapplet is developed for complex calculation used in multiple mappings. In summary, a mapping defines the flow of data from source to target, while a mapplet is a set of transformations that can be reused in multiple mappings.