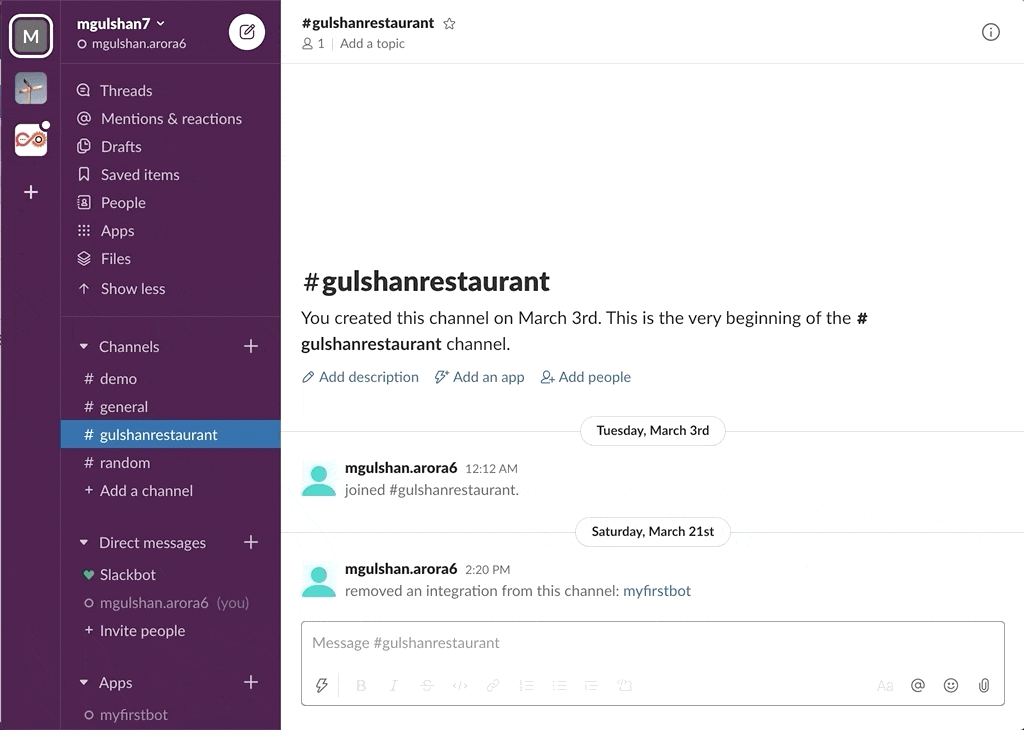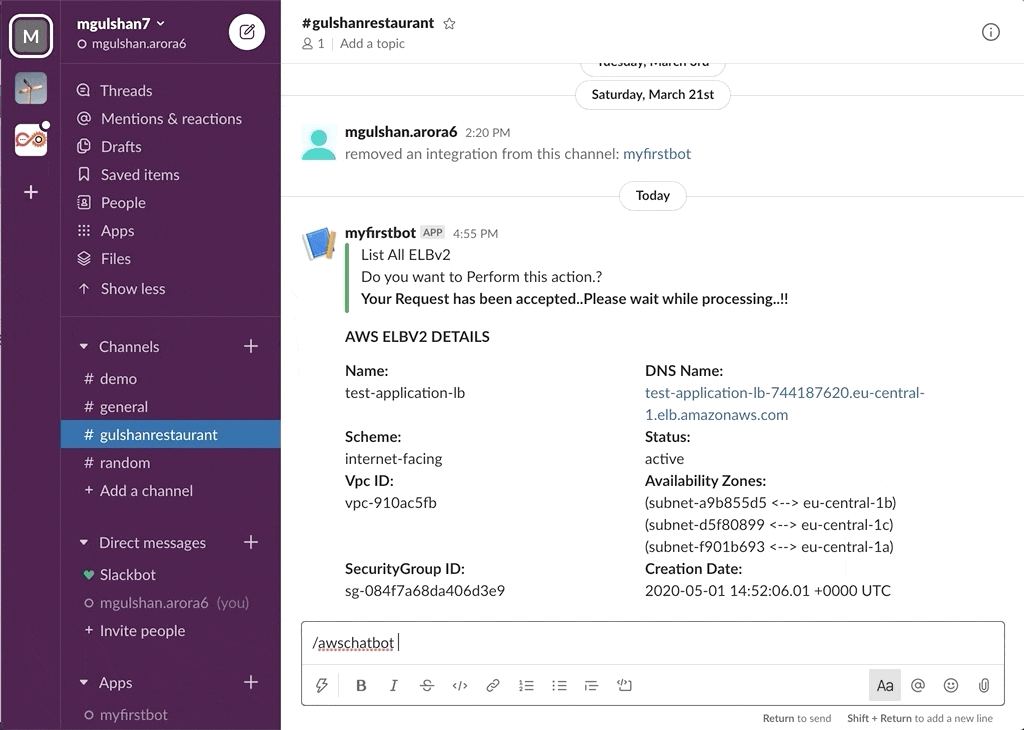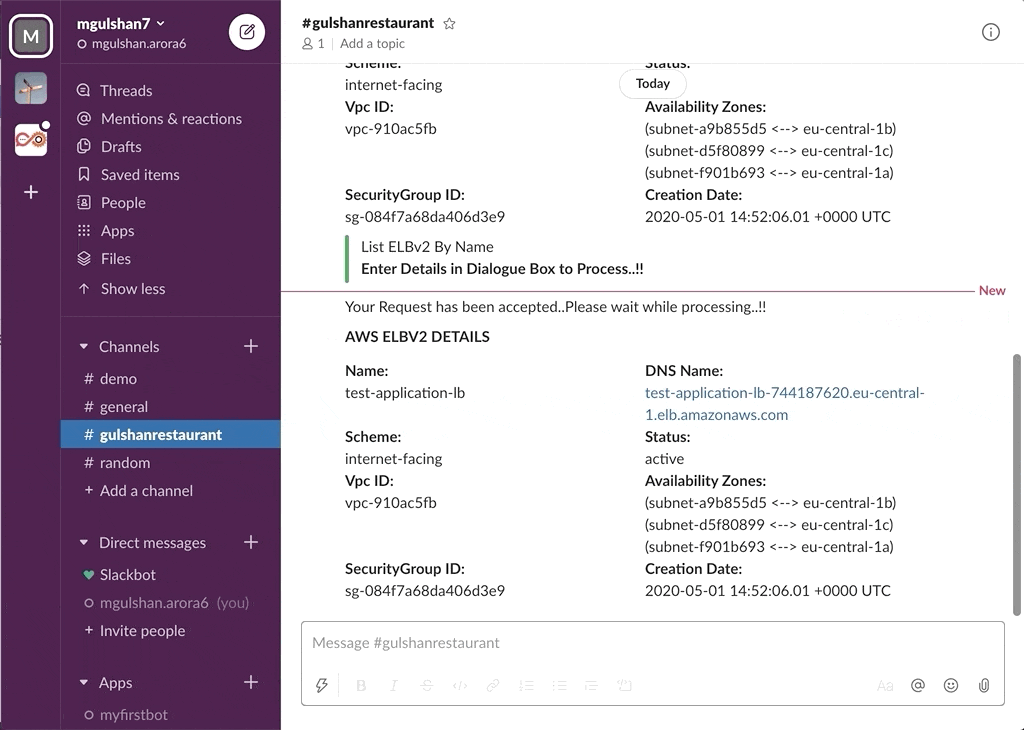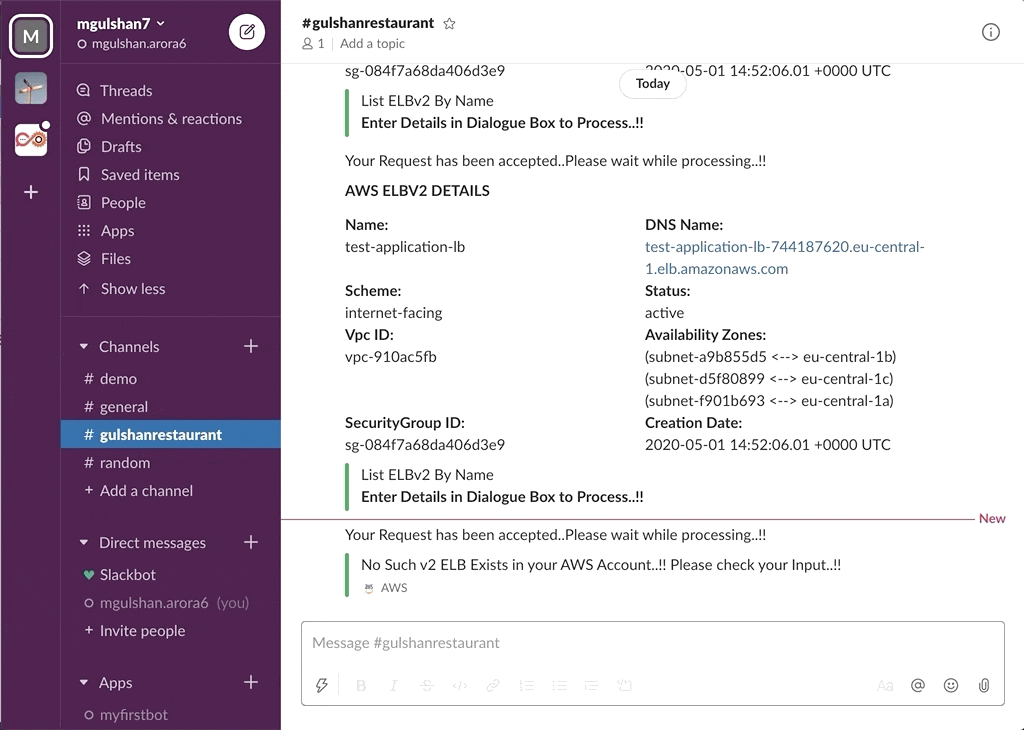
Slack Project --> AWS ChatBot
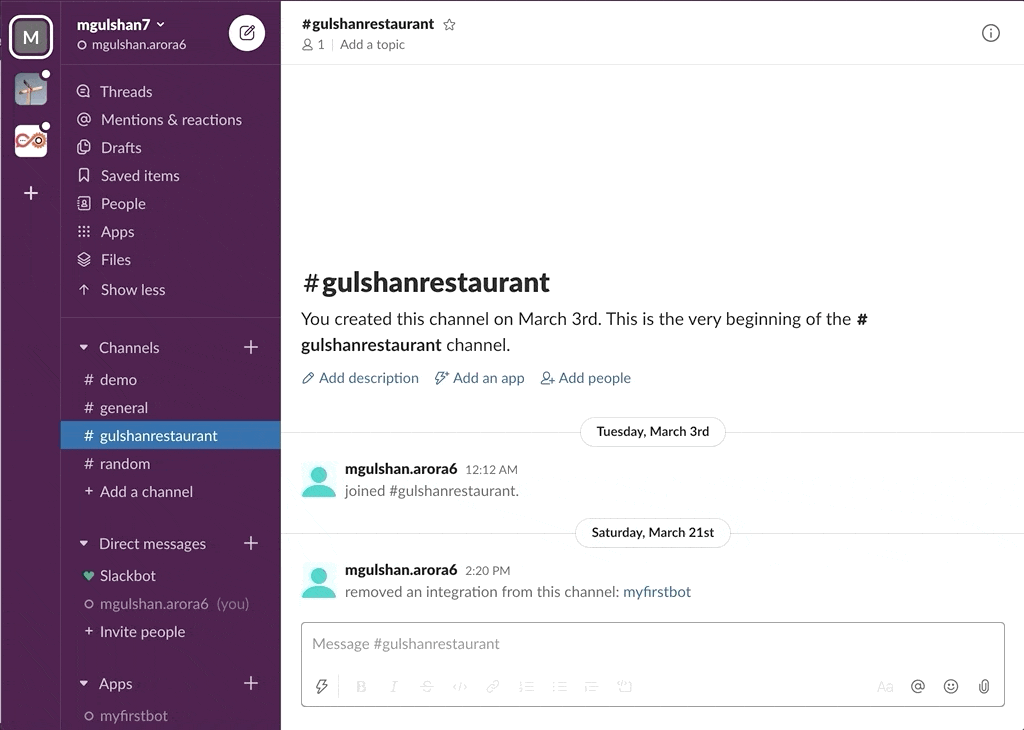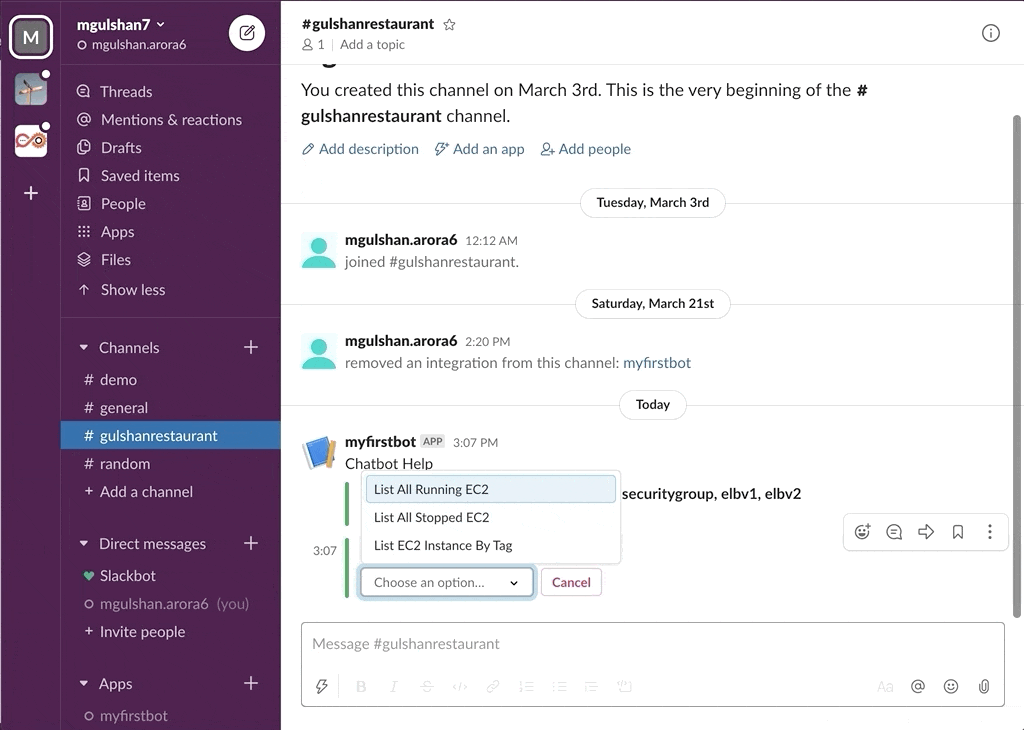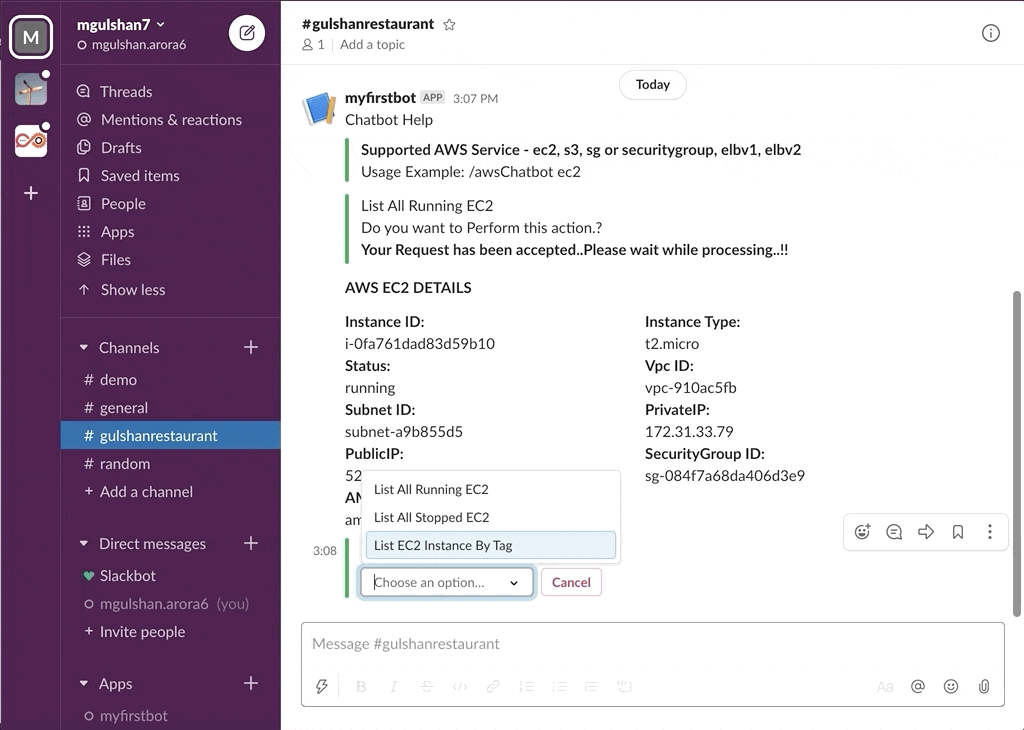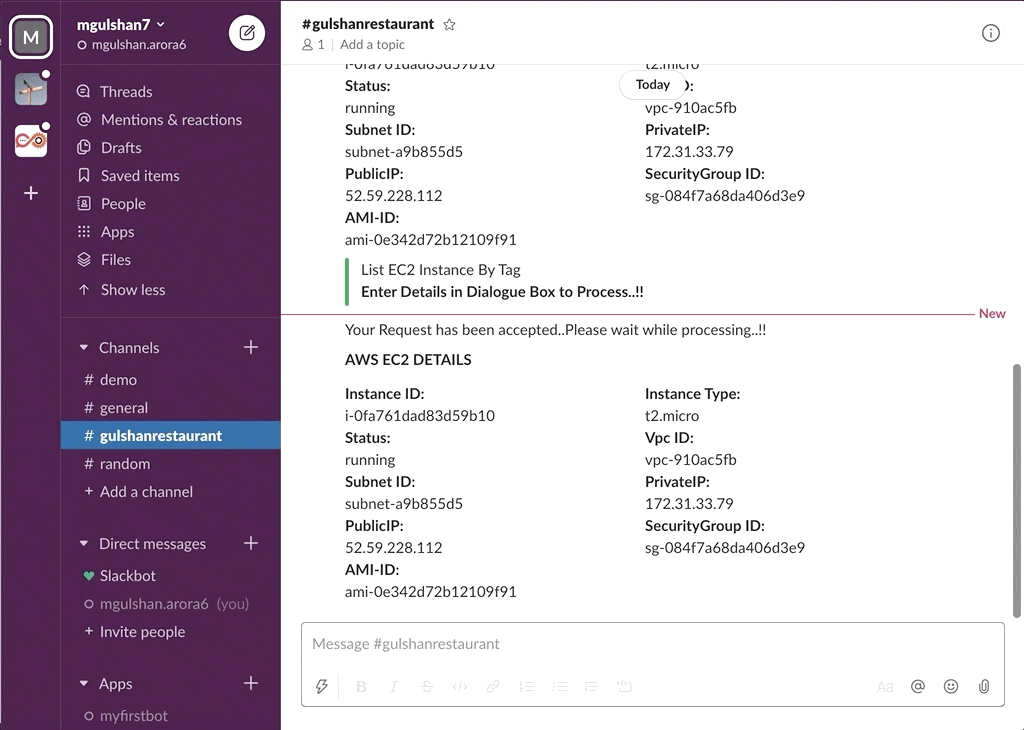
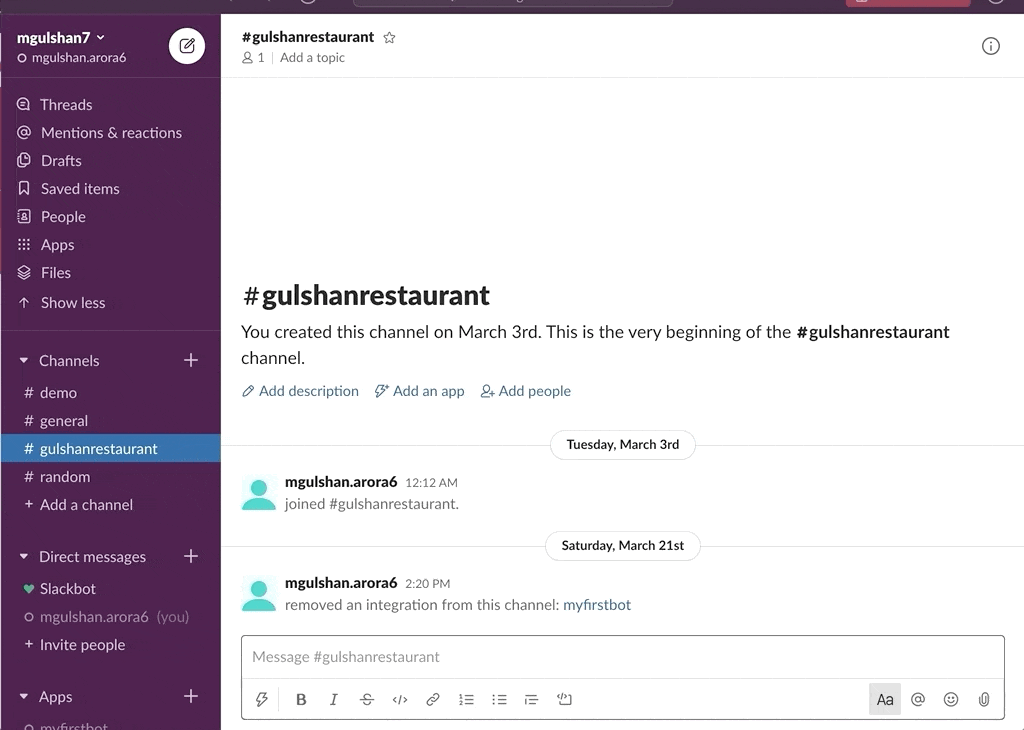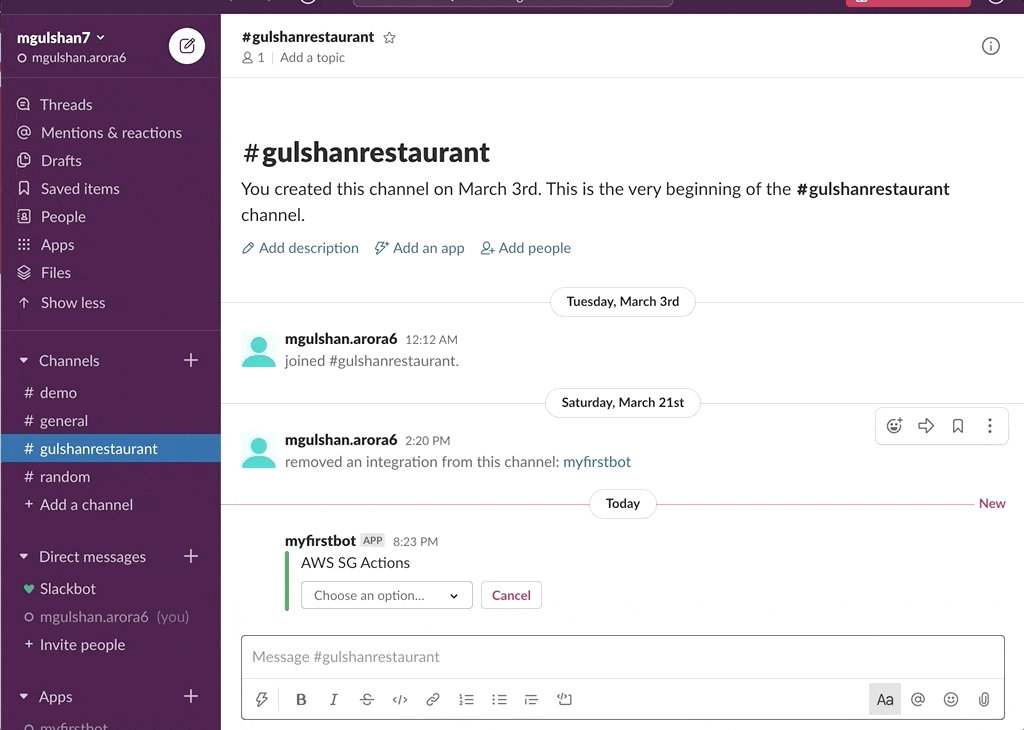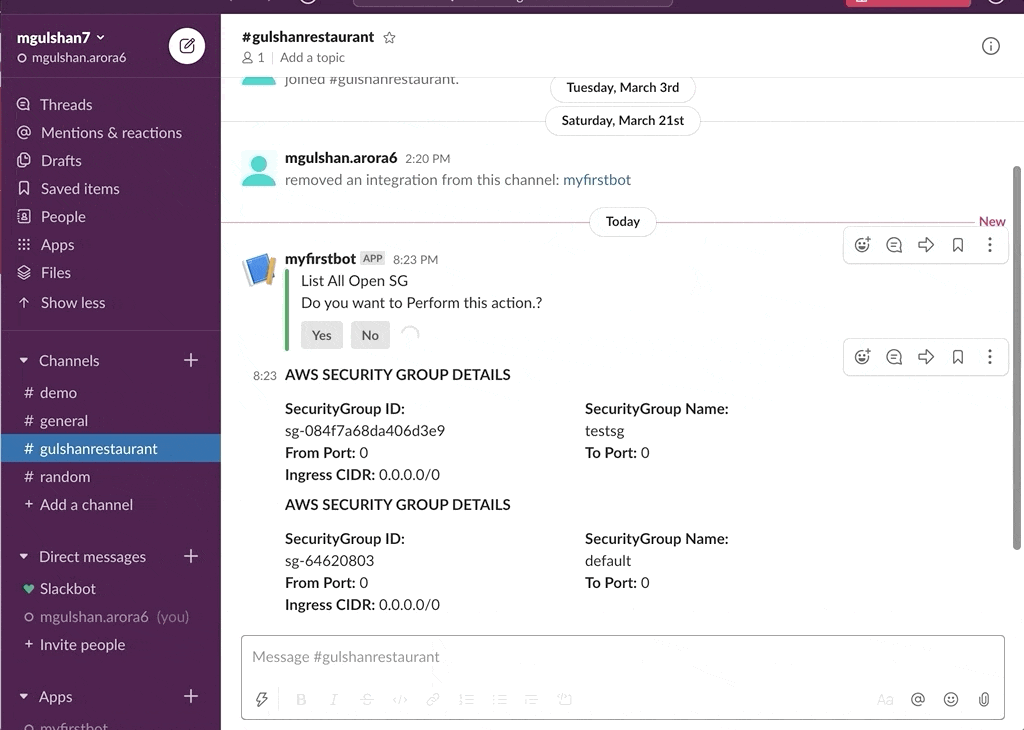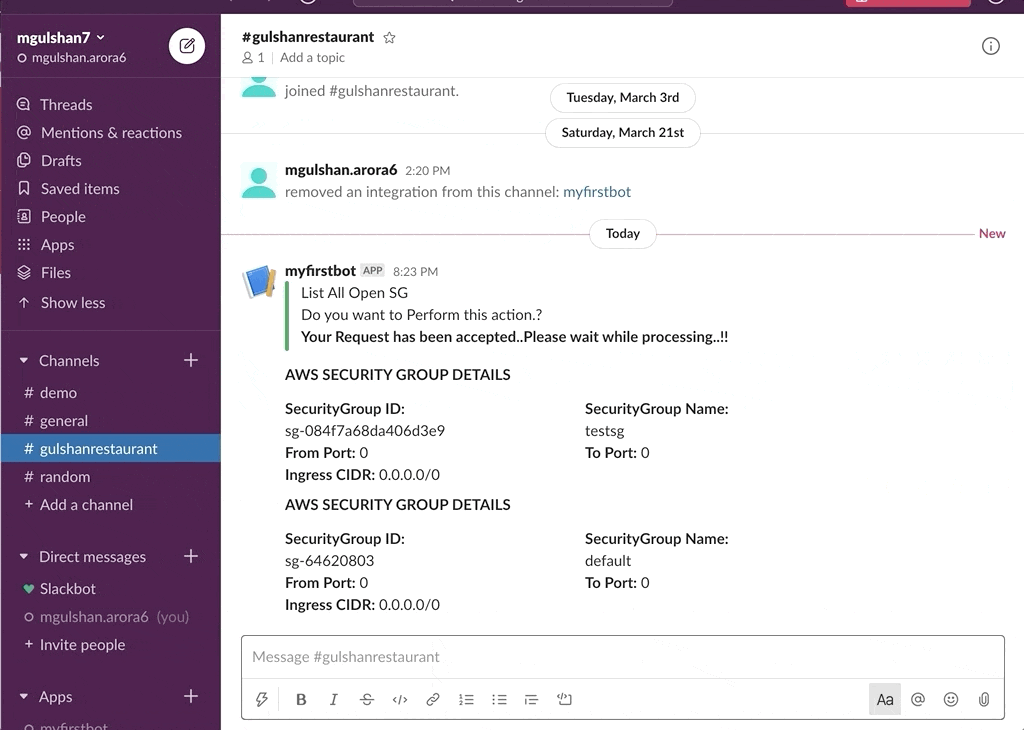
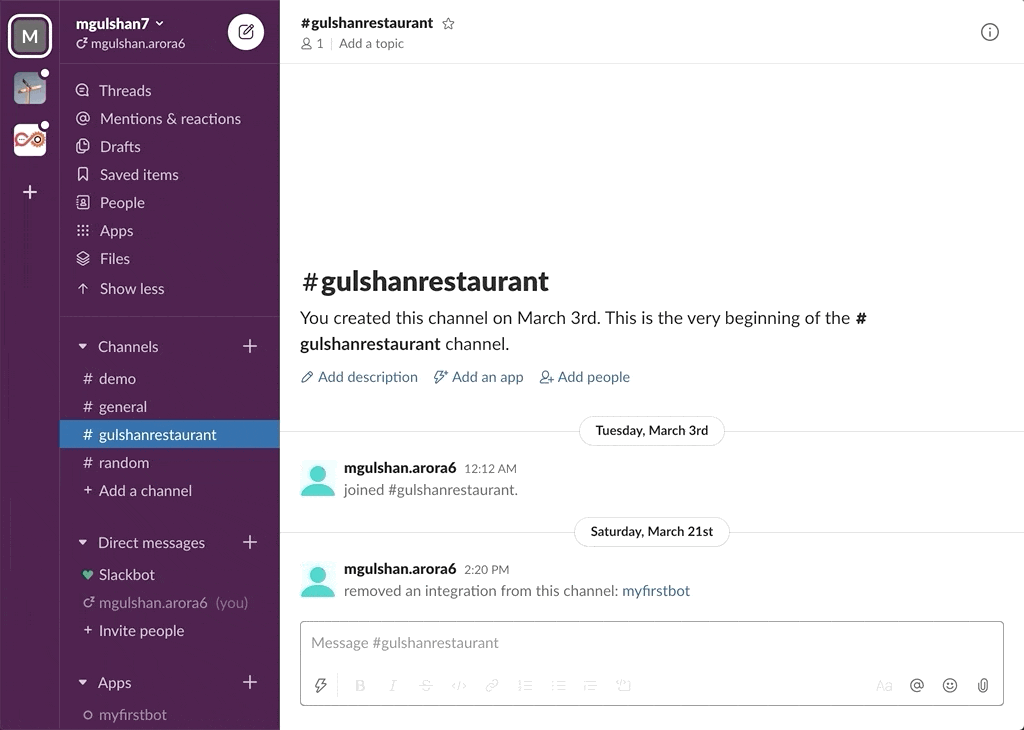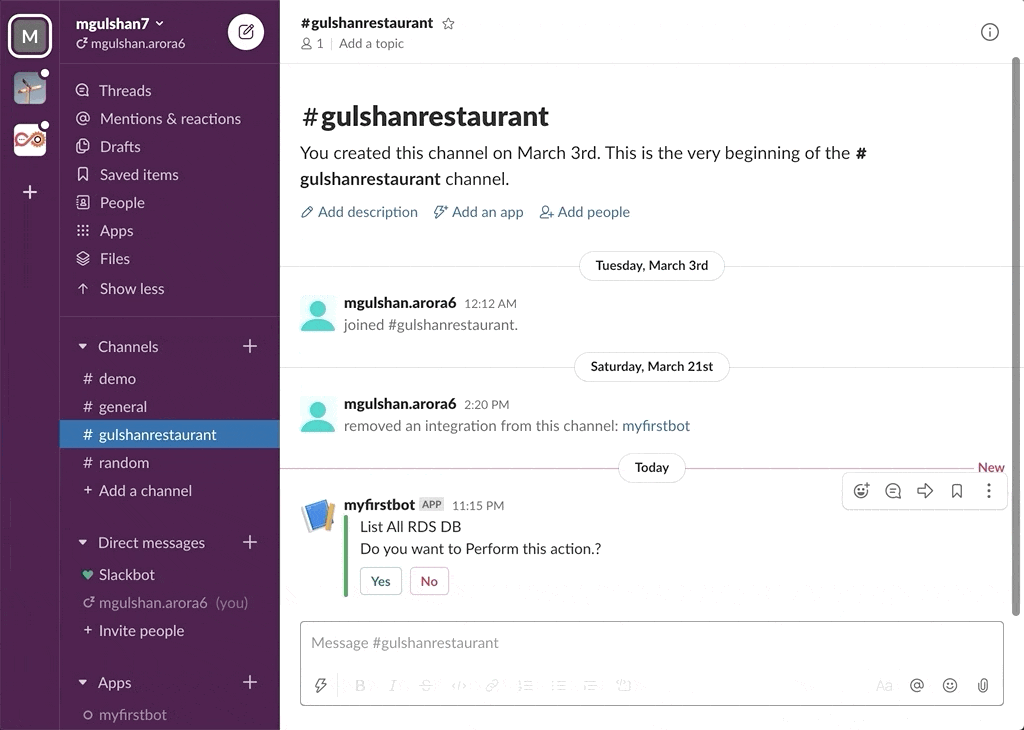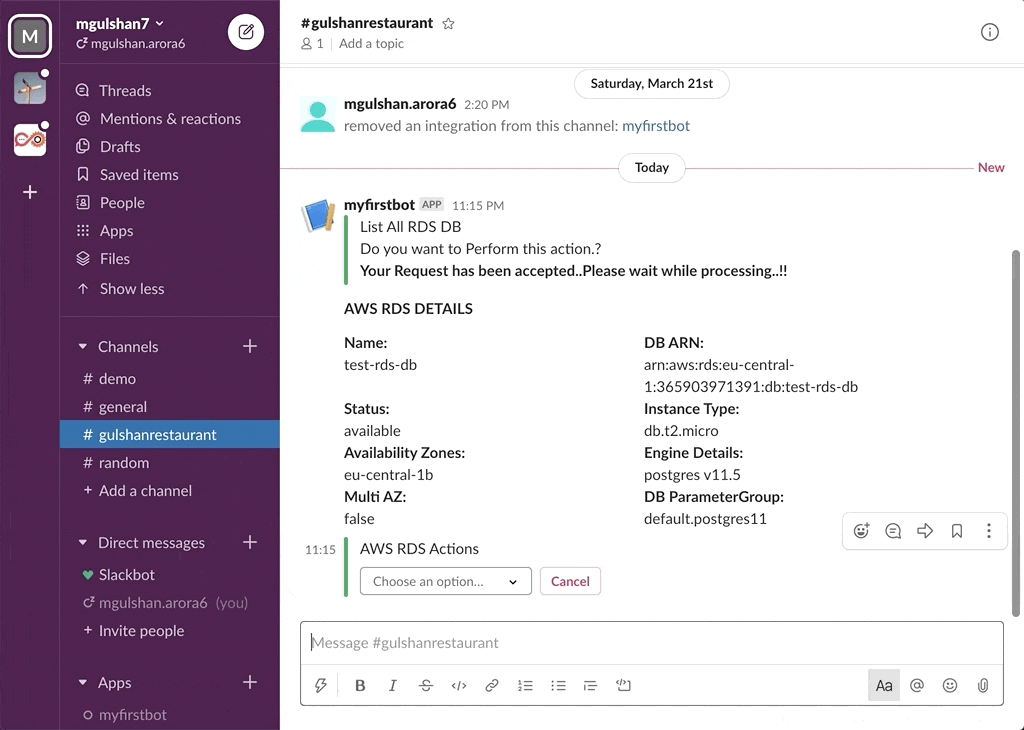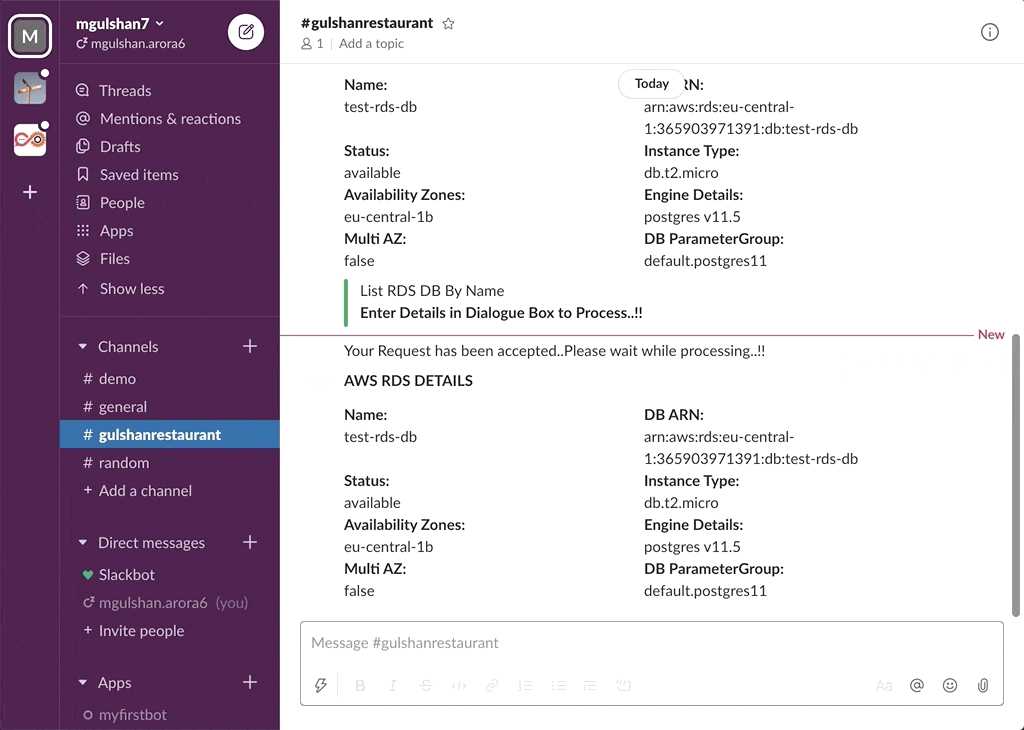
awsChatbot can listen to slash commands initiated by user from configured slack channel to interact with supported AWS services and provide required result. Currently it supports AWS Services like EC2, S3, SecurityGroup, ELBv1, ELBv2, RDS DB.
- AWS EC2
- AWS S3
- AWS SecurityGroup
- AWS ELBv1 (Classic LoadBalancer)
- AWS ELBv2 (Application or Network LoadBalancer)
- AWS RDS DB Instances
go build
./awsChatbot- AWSBOT_PORT : Application Port (default : "9090")
- AWSBOT_DEBUG_AWS_REQUESTS : Debug Request True or False(default : "false")
- AWSBOT_SLASH_COMMAND : Slack Slash Command (default : "/awschatbot")
- AWSBOT_SLACK_SIGNING_SECRET : Slack Signining Secrets.Get one by creating your slack api application from https://api.slack.com/apps
- AWSBOT_SLACK_TOKEN : Slack BOT TOKEN. Get from your application OAuth & Permissions(starts with: xoxb-xxxxxxx)
- AWSBOT_SLACK_CHANNEL : Slack Channel ID. Get it from your slack channel settings
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID : AWS ACCESS KEY ID for IAM User(Can Skip if using IAM Assume Role)
- AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY : AWS SECRET KEY ID for IAM User(Can Skip if using IAM Assume Role)
- AWS_REGION : AWS REGION(default : eu-central-1)
- Locally running kubernetes cluster(minikube) or production running kubernetes cluster in your environment
- Basic kubernetes tools like kubectl (to interact with kubernetes cluster), helm(for deployment)
- CLI terminal to run all the commands
- Access service health-check endpoint from any browser
-
To install kubernetes with minikube
-
To Install kubectl
-
To install Helm(Package Manager) & Tiller(Helm Server) for kubernetes cluster
Important Note:
-
Please configure kubectl command to interact with correct kubernetes cluster using kubernetes-context
-
Get Current Context using below command
kubectl config get-contexts
$ kubectl config get-contexts
CURRENT NAME CLUSTER AUTHINFO NAMESPACE
* minikube minikube minikube
-
docker build -t <image-repository/application-name>:v1.0 .(Build Docker Image) -
docker login && docker push <image-repository/application-name>:v1.0(Push Docker Image) -
kubectl create serviceaccount tiller -n kube-system(Create Service Account for Tiller) -
kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller(Authorize Permission to Tiller) -
helm init --service-account tiller --upgrade(Initialize Helm) -
kubectl create ns awschatbot(Create Kubernetes Namespace) -
kubectl apply -f awschatbot-helm/secrets.yaml -n awschatbot(Create Secrets, Add your base64 secrets in secrets.yaml file) -
helm upgrade --install awschatbot-helm awschatbot-helm --namespace awschatbot(Helm Deploy awschatbot application)
http://localhost:9090/awschatbot/v1/health
- Get EC2 Instance Details
- Get ELB Details
- Get SecurityGroup Details
- Get RDS Details