| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
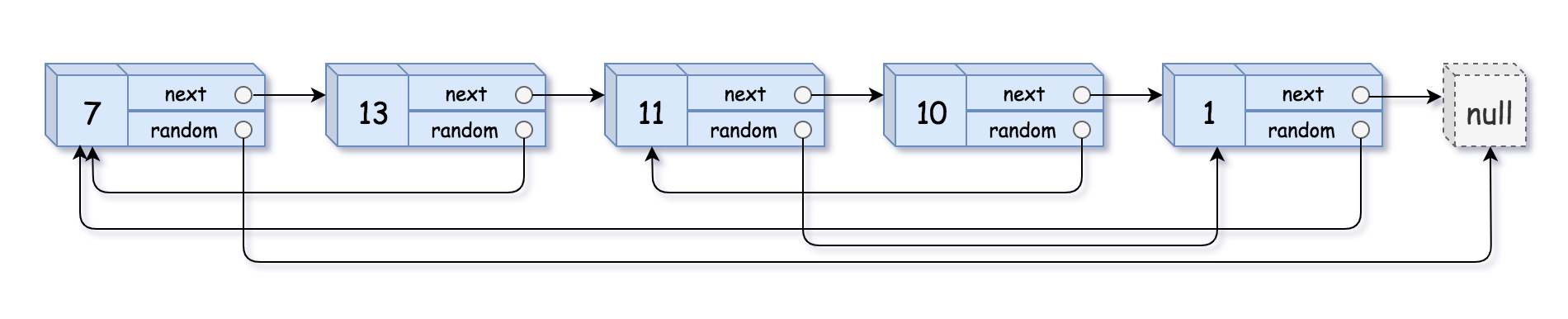
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
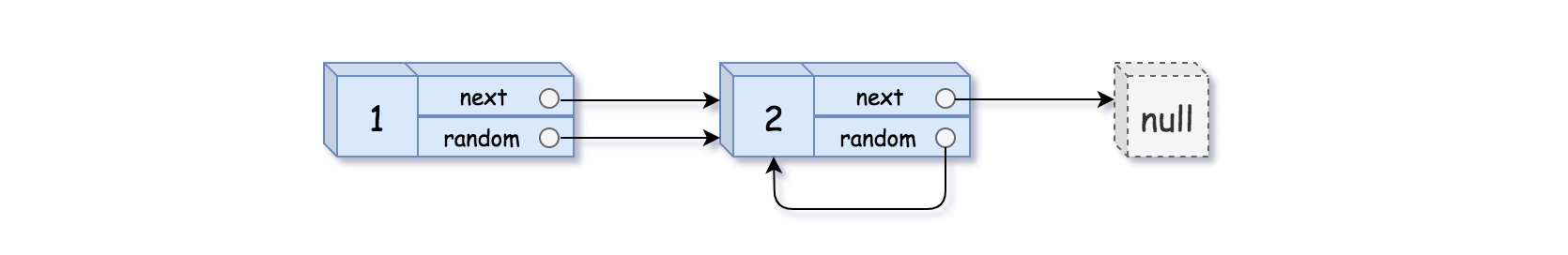
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
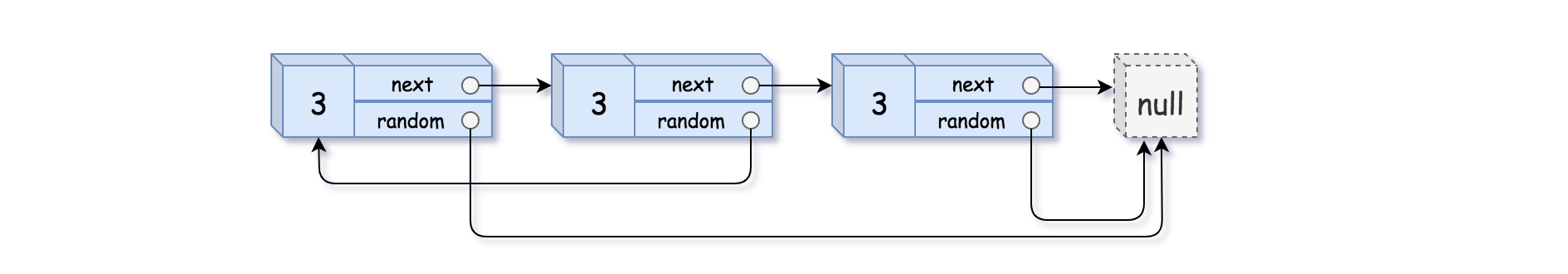
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
提示:
0 <= n <= 1000-104 <= Node.val <= 104Node.random为null或指向链表中的节点。
遍历链表,将链表中的每个节点都复制一份,然后将原节点和复制节点的对应关系存储在哈希表中,同时连接好复制节点的
接下来再遍历链表,根据哈希表中存储的对应关系,将复制节点的
时间复杂度为
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: "Node") -> "Node":
d = {}
dummy = tail = Node(0)
cur = head
while cur:
tail.next = Node(cur.val)
tail = tail.next
d[cur] = tail
cur = cur.next
tail = dummy.next
cur = head
while cur:
tail.random = d.get(cur.random)
tail = tail.next
cur = cur.next
return dummy.next/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Map<Node, Node> d = new HashMap<>();
Node dummy = new Node(0);
Node tail = dummy;
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
tail.next = new Node(cur.val);
tail = tail.next;
d.put(cur, tail);
}
tail = dummy.next;
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
tail.random = d.get(cur.random);
tail = tail.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> d;
Node* dummy = new Node(0);
Node* tail = dummy;
for (auto cur = head; cur; cur = cur->next) {
tail->next = new Node(cur->val);
tail = tail->next;
d[cur] = tail;
}
tail = dummy->next;
for (auto cur = head; cur; cur = cur->next) {
tail->random = d[cur->random];
tail = tail->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Next *Node
* Random *Node
* }
*/
func copyRandomList(head *Node) *Node {
d := map[*Node]*Node{}
dummy := &Node{}
tail := dummy
for cur := head; cur != nil; cur = cur.Next {
tail.Next = &Node{Val: cur.Val}
tail = tail.Next
d[cur] = tail
}
tail = dummy.Next
for cur := head; cur != nil; cur = cur.Next {
tail.Random = d[cur.Random]
tail = tail.Next
}
return dummy.Next
}/**
* Definition for Node.
* class Node {
* val: number
* next: Node | null
* random: Node | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: Node, random?: Node) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* this.random = (random===undefined ? null : random)
* }
* }
*/
function copyRandomList(head: Node | null): Node | null {
const map = new Map<Node, Node>();
let cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.set(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next) ?? null;
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random) ?? null;
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}/**
* // Definition for a Node.
* function Node(val, next, random) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* this.random = random;
* };
*/
/**
* @param {Node} head
* @return {Node}
*/
var copyRandomList = function (head) {
const d = new Map();
const dummy = new Node(0);
let tail = dummy;
for (let cur = head; cur; cur = cur.next) {
tail.next = new Node(cur.val);
tail = tail.next;
d.set(cur, tail);
}
tail = dummy.next;
for (let cur = head; cur; cur = cur.next) {
tail.random = d.get(cur.random);
tail = tail.next;
}
return dummy.next;
};/*
// Definition for a Node.
public class Node {
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node random;
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = null;
random = null;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public Node CopyRandomList(Node head) {
Dictionary<Node, Node> d = new Dictionary<Node, Node>();
Node dummy = new Node(0);
Node tail = dummy;
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
tail.next = new Node(cur.val);
tail = tail.next;
d[cur] = tail;
}
tail = dummy.next;
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
tail.random = cur.random == null ? null : d[cur.random];
tail = tail.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}遍历链表,将链表中的每个节点都复制一份,然后将复制节点插入到原节点的后面。
接下来再遍历链表,根据原节点的
最后再遍历链表,将链表拆分成原链表和复制链表。
时间复杂度为
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: "Node") -> "Node":
if head is None:
return None
cur = head
while cur:
node = Node(cur.val, cur.next)
cur.next = node
cur = node.next
cur = head
while cur:
if cur.random:
cur.next.random = cur.random.next
cur = cur.next.next
ans = head.next
cur = head
while cur:
nxt = cur.next
if nxt:
cur.next = nxt.next
cur = nxt
return ans/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
for (Node cur = head; cur != null;) {
Node node = new Node(cur.val, cur.next);
cur.next = node;
cur = node.next;
}
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next.next) {
if (cur.random != null) {
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
}
}
Node ans = head.next;
for (Node cur = head; cur != null;) {
Node nxt = cur.next;
if (nxt != null) {
cur.next = nxt.next;
}
cur = nxt;
}
return ans;
}
}/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (!head) {
return nullptr;
}
for (Node* cur = head; cur;) {
Node* node = new Node(cur->val);
node->next = cur->next;
cur->next = node;
cur = node->next;
}
for (Node* cur = head; cur; cur = cur->next->next) {
if (cur->random) {
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
}
}
Node* ans = head->next;
for (Node* cur = head; cur;) {
Node* nxt = cur->next;
if (nxt) {
cur->next = nxt->next;
}
cur = nxt;
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Next *Node
* Random *Node
* }
*/
func copyRandomList(head *Node) *Node {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
for cur := head; cur != nil; {
node := &Node{cur.Val, cur.Next, nil}
cur.Next = node
cur = node.Next
}
for cur := head; cur != nil; cur = cur.Next.Next {
if cur.Random != nil {
cur.Next.Random = cur.Random.Next
}
}
ans := head.Next
for cur := head; cur != nil; {
nxt := cur.Next
if nxt != nil {
cur.Next = nxt.Next
}
cur = nxt
}
return ans
}/**
* // Definition for a Node.
* function Node(val, next, random) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* this.random = random;
* };
*/
/**
* @param {Node} head
* @return {Node}
*/
var copyRandomList = function (head) {
if (!head) {
return null;
}
for (let cur = head; cur; ) {
const node = new Node(cur.val, cur.next, null);
cur.next = node;
cur = node.next;
}
for (let cur = head; cur; cur = cur.next.next) {
if (cur.random) {
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
}
}
const ans = head.next;
for (let cur = head; cur; ) {
const nxt = cur.next;
if (nxt) {
cur.next = nxt.next;
}
cur = nxt;
}
return ans;
};/*
// Definition for a Node.
public class Node {
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node random;
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = null;
random = null;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public Node CopyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; ) {
Node node = new Node(cur.val, cur.next);
cur.next = node;
cur = node.next;
}
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next.next) {
if (cur.random != null) {
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
}
}
Node ans = head.next;
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; ) {
Node nxt = cur.next;
if (nxt != null) {
cur.next = nxt.next;
}
cur = nxt;
}
return ans;
}
}