Binary trees are chosen over other more primary data structures because you can search a binary tree very quickly (as opposed to a linked list, for example) and you can quickly insert and delete data from a binary tree (as opposed to an array).
common operations you can perform on graphs:
Additions
insert: insert a node to tree, if the node is lower than the root it place it to left otherwise to the right
Removals
remove: removes a node from the tree
Search
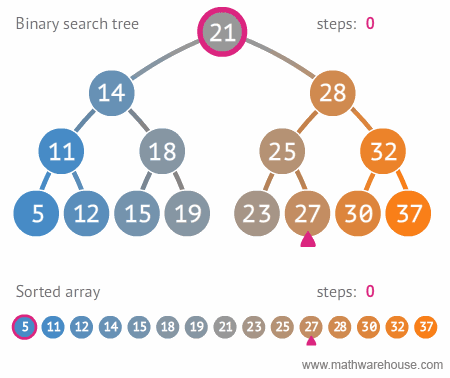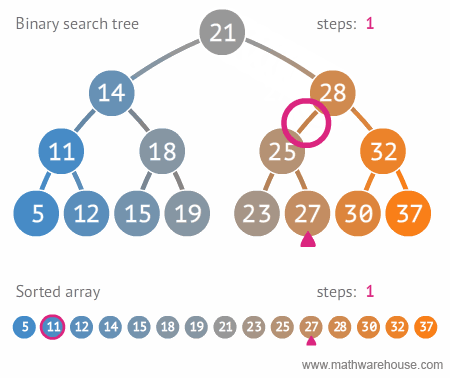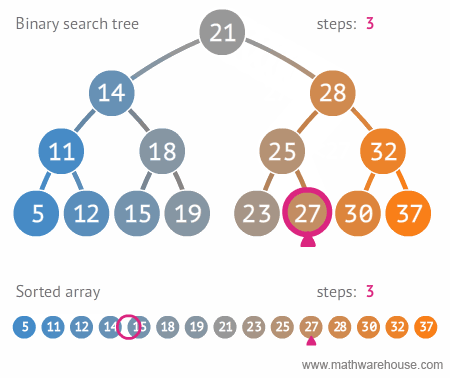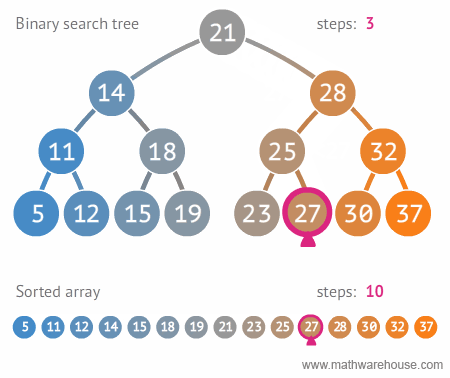
find: Search for a specific valuemaxValue: Search for the minimum valueminValue: Search for the maximum value
Traversals
inOrder: In this traversal method, the left subtree is visited first, then the root and later the right sub-treepreOrder: In this traversal method, the root node is visited first, then the left subtree and finally the right subtree.postOrder: In this traversal method, the root node is visited last, hence the name. First we traverse the left subtree, then the right subtree and finally the root node.
Display
show: displays the node data
- Binary Search Tree - Used in many search applications where data is constantly entering/leaving, such as the map and set objects in many languages' libraries.
- Binary Space Partition - Used in almost every 3D video game to determine what objects need to be rendered.
- Binary Trees - Used in almost every high-bandwidth router for storing router-tables.
- Hash Trees - used in p2p programs and specialized image-signatures in which a hash needs to be verified, but the whole file is not available.
- Heaps - Used in implementing efficient priority-queues, which in turn are used for scheduling processes in many operating systems, Quality-of-Service in routers, and A* (path-finding algorithm used in AI applications, including robotics and video games). Also used in heap-sort.