-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 84
[ES6] Promises(1): the API
이 문서는 http://www.2ality.com/2014/10/es6-promises-api.html 를 번역한 내용입니다.
#목차
이번 포스트는 일반적인 promise를 통한 비동기 프로그래밍과 ES6 promise API에 일부를 소개하고자 합니다. 2개의 비동기 프로그래밍 포스트중 2번째이며, 충분히 이해하기 위해선 1번째 포스트를 읽어보는것이 좋을 것입니다.
#1. Promises
Promises는 비동기 프로그래밍의 한부분을 도와주는 패턴입니다.(:함수 또는 메서드를 비동기적으로 결과를 받는 것) 이런 기능을 구현하기 위해선 당신은 결과를 위해 지정해 놓은 객체인(an object that is a placeholder for the result) promise 를 반환해야합니다.
함수 호출자는 연산된 결과를 알려주는 promise와 함께 콜백을 등록합니다.(The caller of the function registers callbacks with the promise to be notified once the result has been computed) 이 함수는 promise를 통해 결과를 전송합니다.
자바스크립트 promises의 사실상 표준은 Promises/A+ 이라고 부릅니다. ECMAScript6 promise API는 표준을 따릅니다.
#2. 첫번째 예제
첫번째 예제를 봅시다, to give you a taste of what working with promises is like.
Node-js스타일 콜백으로 비동기적으로 파일 읽는 법은 다음과 같습니다.
fs.readFile('config.json',
function (error, text) {
if (error) {
console.error('Error while reading config file');
} else {
try {
var obj = JSON.parse(text);
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj, null, 4));
} catch (e) {
console.error('Invalid JSON in file');
}
}
});같은 기능을 promise 로 구현하면 다음과 같습니다.
readFilePromisified('config.json')
.then(function (text) { // (A)
var obj = JSON.parse(text);
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj, null, 4));
})
.catch(function (reason) { // (B)
// File read error or JSON SyntaxError
console.error('An error occurred', reason);
});promise도 여전히 콜백이 존재합니다. 그러나 promise는 결과를 호출 할 수 있는 메서드를 통해 제공됩니다.(then(),catch()) (B)라인안에 error 콜백은 2가지의 편리성을 가지고 있습니다. 첫 번째, 에러 처리를 한가지 방식으로 할 수 있습니다. 두 번째로, 당신은 readFilePromisified()와 (A)라인의 콜백 둘다 에러를 핸들링 할 수 있습니다.
#3.Promises 생성과 사용
promise가 어떻게 작동하는지 공급자(Producer)와 소비자(consumer) 측면에서 알아 봅시다.
공급자로써, promise를 생성하고 결과를 전송합니다.
var promise = new Promise(
function (resolve, reject) { // (A)
...
if (...) {
resolve(value); // success
} else {
reject(reason); // failure
}
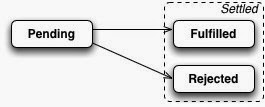
});promise는 항상 아래 3가지 상태중(상호배타적인) 1가지 상태 입니다.
- 대기(pending) : 아직 결과 처리가 안됬다.
- 성공(Fulfilled) : 성공적으로 완료되었다.
- 거절(rejected) : 처리되는 동안 실패가 발생하였다.
promise는 성공(fulfilled)이나 거절(rejected)중 하나로 고정 됩니다.(연산이 끝났을 때) (A promise is settled (the computation it represents has finished) if it is either fulfilled or rejected.) promise 상태는 한번만 지정되며, 그 후 상태를 유지합니다. 그 후에 상태를 바꾸려고 해도 아무 변화가 없습니다.
new Promise()의 파라미터는( (A)라인 시작점 ) 집행자(executor 모호한 단어라 이하 영문표기로 명칭)라고 부릅니다.
- 만약 연산가 잘 되었다면, executor는
resolve()통해 결과를 전송 합니다. 보통 promise 성공(fulfills)을 말합니다.(promise가 resolve였지만 실제로 아닐 경우 뒤에 설명하겠습니다.) - 만약 에러가 발생할 경우, executor는
reject()를 통해 promise-소비자(consumer)에게 통보 합니다. 즉 항상 promise는 거절(reject)합니다.
- 번역 문서를 읽는 중, 오타나 어색한 문장이 있으면 이슈를 등록해주세요!